Transcriptome-Metabolome Analysis Reveals That Crossbreeding Improves Meat Quality in Hu Sheep and Their F1-Generation Sheep
- PMID: 40282783
- PMCID: PMC12026837
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14081384
Transcriptome-Metabolome Analysis Reveals That Crossbreeding Improves Meat Quality in Hu Sheep and Their F1-Generation Sheep
Abstract
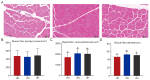
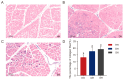
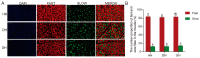
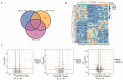
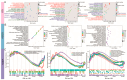
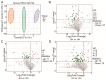
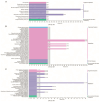
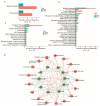
Consumers are increasingly demanding higher-quality mutton. Crossbreeding has been recognized as an effective means to improve meat quality. However, the phenomenon underlying these molecular system mechanisms remains largely unidentified. In this study, 48 male lambs aged 3 months were selected, including ♂ Hu sheep × ♀ Hu (HH, n = 16), ♂ Polled Dorset × ♀ Hu sheep F1 hybrid lambs (DH, n = 16), and ♂ Southdown × ♀ Hu sheep (SH, n = 16) F1 hybrid lambs, and raised in a single pen under the same nutritional and management conditions for 95 days. Then, seven sheep close to the average weight of the group were selected and fasted for 12 h prior to slaughter. By comparing the muscle fiber characteristics of the Longissimus dorsi of the three groups of sheep, and through transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses, we revealed molecular differences in the meat quality of Hu sheep crossbred with different parent breeds. The results of this study showed that muscle fiber diameter and cross-sectional area were significantly greater in the DH group than in the HH group, and collagen fiber content in the DH group was also significantly higher than in the HH group (p < 0.05). A total of 163 differential genes and 823 differential metabolites were identified in the three groups, most of which were related to muscle development and lipid metabolism. These included the AMPK signaling pathway, the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, glycerophospholipid metabolism, and the related genes EFHB, PER3, and PPARGC1A. The results of this study offer valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying the impact of crossbreeding on meat quality and provide a theoretical foundation for sheep crossbreed production.
Keywords: crossbreed; longissimus dorsi; meat quality; metabolomics; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
- CAAS-ZDRW202502/the Major Scientific Research Task of the Science and Technology Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciencesx
- 22ZD6NA037, 21ZD11NM001/the Science and Technology Program of Gansu Province
- Y2024YJ08, 1610322024020/the Central Public interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund
- GYGG-2024-6/the Seed Industry Breakthrough Project of Gansu Province
- HNK 2023-09/the Science and Technology Bureau Project of Huan County
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

