Recent Advances in Polysaccharides from Cornus officinalis: Extraction, Purification, Structural Features, and Bioactivities
- PMID: 40282816
- PMCID: PMC12026513
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14081415
Recent Advances in Polysaccharides from Cornus officinalis: Extraction, Purification, Structural Features, and Bioactivities
Abstract
Cornus officinalis, as a medicinal plant, is rich in biologically active components, including polysaccharides, flavonoids, triterpenoids, and organic acids, which offer a variety of health benefits and significant potential for development in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Cornus officinalis polysaccharides (COPs) are considered among the primarily functional ingredients of the plant and are abundant in bioactivities. The present paper reviews the research conducted on the extraction, purification, structural properties, and biological activities of COPs. It also provides an overview of future development prospects, with a view to offering reference material for further development and research on COPs. In addition, the paper makes recommendations regarding theoretical preparations for the exploration of the application potential of COPs in the food industry and various other industrial fields.
Keywords: Cornus officinalis; activity; polysaccharides; structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competitive financial interests or personal relationships that could influence the work reported in this article.
Figures



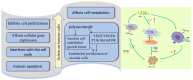



References
-
- Fan Q., Cheng X.B., Rong L., Zhang C.X. Research progress on chemical constituents, bioactivities, formula applications and quality control of Cornus officinalis. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2020;32:1244–1258. doi: 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2020.7.021. - DOI
-
- Yang X.L., Sun H.Q., He C.F., Lu L.S., Kang J.F. Analysis of amino acid composition and nutritional evaluation of Corni Fructus from different habitats. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2022;13:7200–7209. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2022.22.004. - DOI
-
- Peng Z.C., Wang Y.M., He J., Zhang J., Pan X.G., Ye X.S., Zhang W.K., Xu J.K. Chemical constituents and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities from edible Cornus officinalis fruits. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022;248:1003–1010. doi: 10.1007/s00217-021-03940-6. - DOI
-
- Li M.L., Wang P., Yin C., Zan J.F., Yang K., Chen L.L., Liu J.F. Pharmacodynamic evaluation and mechanism study of Corni Fructus polysaccharide on anti-aging of Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2022;13:6996–7003. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2022.21.025. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

