Appropriate Distraction Strength for Metatarsophalangeal Joint Arthroscopy
- PMID: 40282945
- PMCID: PMC12028850
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61040654
Appropriate Distraction Strength for Metatarsophalangeal Joint Arthroscopy
Abstract
Background and Objectives: To investigate the natural metatasophalangeal (MTP) joint distance, we studied the appropriate degree of distraction for arthroscopy and the associated factors, including age, gender, and body mass index (BMI). Materials and Methods: Sixty-seven patients who underwent MTP joint arthroscopy or foot and ankle surgery from April 2013 to June 2020 were enrolled. Foot plain radiographs were taken using a mini-fluoroscan with no traction, manual traction, and traction of 5 pounds, 10 pounds, and 15 pounds to measure the MTP joint distance. Age, gender, and BMI were compared as associated factors. The minimum joint distance of MTP joint arthroscopy was defined as 2.8 mm, which was the sheath size of a 1.9 mm, 30° high-definition arthroscope. Results: Regarding natural MTP joint space sizes, the MTP-2 joint had the largest joint size (2.39 ± 0.37 mm). The MTP-5 joint had the smallest joint size (1.59 ± 0.34 mm). Traction of 10 lb was an appropriate distraction force for the MTP-1 joint (3.09 ± 0.03 mm) and MTP-4 joint (3.07± 0.47 mm) in arthroscopy. Traction of 5lb was an appropriate distraction force for the MTP-2 (3.32 ± 0.60 mm), MTP-3 (2.89 ± 0.50 mm), and MTP-5 (2.97 ± 0.49 mm) joints. For the MTP-1 and MTP-4 joints, males had significantly greater joint space sizes than females for no traction (p = 0.039), manual traction (p = 0.002), and traction of 5 pounds (p = 0.004), 10 pounds, (p = 0.013), and 15 pounds (p = 0.024). There was no statistically significant difference in joint space size according to age or BMI for any MTP joints (p > 0.05). Conclusions: Among natural joint spaces without traction, the MTP-2 joint had the largest joint size while the MTP-5 joint had the smallest joint size. In MTP joint arthroscopy, a traction power of 10 lb is sufficient for appropriate distraction of all MTP joints. Less distraction power is required for males than for females, especially for the MTP-1 and MTP-4 joints.
Keywords: MTP joint arthroscopy; distraction; foot ankle surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
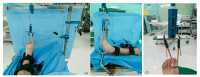
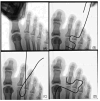
Similar articles
-
Lesser metatarsal phalangeal joint arthroscopy: anatomic description and comparative dissection.Arthroscopy. 2014 Aug;30(8):971-9. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2014.03.018. Epub 2014 May 14. Arthroscopy. 2014. PMID: 24835840
-
Distraction Gap Needed for Safe Central Compartment Access in Hip Arthroscopy.Am J Sports Med. 2023 Apr;51(5):1211-1216. doi: 10.1177/03635465231160179. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Am J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 36939194
-
Traction versus distension for distraction of the joint during hip arthroscopy.Arthroscopy. 1997 Jun;13(3):346-9. doi: 10.1016/s0749-8063(97)90032-3. Arthroscopy. 1997. PMID: 9195032
-
Hallux metatarsophalangeal arthroscopy: indications and techniques.Foot Ankle Clin. 2015 Mar;20(1):109-22. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2014.10.012. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Foot Ankle Clin. 2015. PMID: 25726487 Review.
-
Arthroscopy of the hallux metatarsophalangeal joint.Foot Ankle Clin. 2000 Sep;5(3):715-24. Foot Ankle Clin. 2000. PMID: 11232405 Review.
References
-
- Canale S.T. Arthroscopy of the foot and ankle. In: Canale S.T., Beaty J.H., editors. Campbell’s Operative Orthopaedics. 12th ed. Mosby; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2013.
-
- Derner R., Naldo J. Small joint arthroscopy of the foot. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2011;28:551–560. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

