Comparative Analysis of Cardiac SPECT Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: Full-Ring Solid-State Detectors Versus Dedicated Cardiac Fixed-Angle Gamma Camera
- PMID: 40282956
- PMCID: PMC12028854
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61040665
Comparative Analysis of Cardiac SPECT Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: Full-Ring Solid-State Detectors Versus Dedicated Cardiac Fixed-Angle Gamma Camera
Abstract
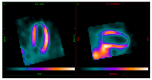
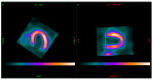
Background and Objectives: Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) is a well-established technique for evaluating myocardial perfusion and function in patients with suspected or known coronary artery disease. While conventional dual-detector SPECT scanners have limitations in spatial resolution and photon detection sensitivity, recent advancements, including full-ring solid-state cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) detectors, offer enhanced image quality and improved diagnostic accuracy. This study aimed to compare the performance of Veriton-CT, a full-ring CZT SPECT system, with GE Discovery 530c, a dedicated cardiac fixed-angle gamma camera, in myocardial perfusion imaging and their correlation with coronary angiography findings. Materials and Methods: This was a prospective study that analyzed 21 patients who underwent MPI at the Department of Nuclear Medicine, Lithuanian University of Health Sciences, Kauno Klinikos. A one-day stress-rest protocol using 99mTc-Sestamibi was employed, with stress testing performed via bicycle ergometry or pharmacological induction. MPI was first conducted using GE Discovery 530c (GE Health Care, Boston, MA, USA), followed by imaging on Veriton-CT, which included low-dose CT for attenuation correction. The summed stress score (SSS), summed rest score (SRS), and summed difference score (SDS) were analyzed and compared between both imaging modalities. Coronary angiography results were retrospectively collected, and lesion-based analysis was performed to assess the correlation between imaging results and the presence of significant coronary artery stenosis (≥35% and ≥70% narrowing). Image quality and the certainty of distinguishing the inferior myocardial wall from extracardiac structures were also evaluated by two independent researchers with differing levels of experience. Results: Among the 14 patients included in the final analysis, Veriton-CT was more likely to classify MPI scans as normal (64.3%) compared to GE Discovery 530c (28.6%). Additionally, Veriton-CT provided a better assessment of the right coronary artery (RCA) basin, showing greater agreement with coronary angiography findings than GE Discovery 530c, although the difference was not statistically significant. No significant differences in lesion overlap were observed for the left anterior descending artery (LAD) or left circumflex artery (LCx) basins. Furthermore, the image quality assessment revealed slightly better delineation of extracardiac structures using Veriton-CT (Spectrum Dynamics Medical, Caesarea, Israel), particularly when evaluated by an experienced researcher. However, no significant difference was observed when assessed by a less experienced observer. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that Veriton-CT, with its full-ring CZT detector system, may offer advantages over fixed-angle gamma cameras in improving image quality and reducing attenuation artifacts in MPI. Although the difference in correlations with coronary angiography findings was not statistically significant, Veriton-CT showed a trend toward better agreement, particularly in the RCA basin. These results indicate that full-ring SPECT imaging could improve the diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive MPI, potentially reducing the need for unnecessary invasive angiography. Further studies with larger patient cohorts are required to confirm these findings and evaluate the clinical impact of full-ring SPECT technology in myocardial perfusion imaging.
Keywords: cardiac SPECT MPI; dedicated cardiac fixed-angle gamma camera; full-ring solid-state detectors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vrints C.J., Andreotti F., Koskinas K.C., Rossello X., Adamo M., Ainslie J., Banning A.P., Budaj A., Buechel R.R., Chiariello G.A., et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2024;45:3415–3537. - PubMed
-
- Adnan G., Rahman M.N. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Nuclear Medicine SPECT Scan Cardiovascular Assessment, Protocols, and Interpretation. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources