The Role of Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 40282981
- PMCID: PMC12028963
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61040689
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
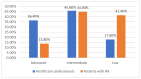
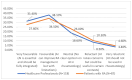
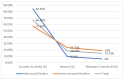
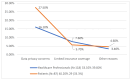
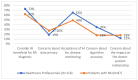
Background and Objectives: Artificial intelligence has emerged as a transformative tool in healthcare, offering capabilities such as early diagnosis, personalised treatment, and real-time patient monitoring. In the context of rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic autoimmune disease that demands timely intervention, artificial intelligence shows promise in overcoming diagnostic delays and optimising disease management. This study examines the role of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis, focusing on perceived benefits, challenges, and acceptance levels among healthcare professionals and patients. Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted using a detailed questionnaire distributed to 205 participants, including rheumatologists, general practitioners, and rheumatoid arthritis patients from Romania. The study used descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, and logistic regression to analyse AI acceptance in rheumatology. Data visualisation and multiple imputations addressed missing values, ensuring accuracy. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05 for hypothesis testing. Results: Respondents with prior experience in artificial intelligence perceived it as more useful for early diagnosis and personalised management of RA (p < 0.001). Familiarity with artificial intelligence concepts positively correlated with acceptance in routine rheumatology practice (ρ = 1.066, p < 0.001). The main barriers identified were high costs (36%), lack of medical staff training (37%), and concerns regarding diagnostic accuracy (21%). Although less frequently mentioned, data privacy concerns remained relevant for a subset of respondents. The study revealed that artificial intelligence could improve diagnostic accuracy and rheumatoid arthritis monitoring, being perceived as a valuable tool by professionals familiar with digital technologies. However, 42% of participants cited the lack of data standardisation across medical systems as a major barrier, underscoring the need for effective interoperability solutions. Conclusions: Artificial intelligence has the potential to revolutionise rheumatoid arthritis management through faster and more accurate diagnoses, personalised treatments, and optimised monitoring. Nevertheless, challenges such as costs, staff training, and data privacy need to be addressed to ensure efficient integration into clinical practice. Educational programmes and interdisciplinary collaboration are essential to increase artificial intelligence adoption in rheumatology.
Keywords: artificial intelligence rheumatoid arthritis; diagnosis; digital technologies rheumatoid arthritis; management of rheumatoid arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Soori M., Arezoo B., Dastres R. Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Advanced Robotics, a Review. Cogn. Robot. 2023;3:54–70.
-
- Taye M.M. Understanding of Machine Learning with Deep Learning: Architectures, Workflow, Applications and Future Directions. Computers. 2023;12:91. doi: 10.3390/computers12050091. - DOI
-
- Morabito F.C., Kozma R., Alippi C., Choe Y. Artificial Intelligence in the Age of Neural Networks and Brain Computing. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2024. Advances in AI, Neural Networks, and Brain Computing: An Introduction; pp. 1–8.
-
- Singh A.P., Saxena R., Saxena S., Maurya N.K. Artificial Intelligence Revolution in Healthcare: Transforming Diagnosis, Treatment, and Patient Care. Asian J. Adv. Res. 2024;7:241–263.
-
- Asif S., Wenhui Y., ur-Rehman S., ul-Ain Q., Amjad K., Yueyang Y., Awais M. Advancements and Prospects of Machine Learning in Medical Diagnostics: Unveiling the Future of Diagnostic Precision. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2024:1–31.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

