Pathological Investigation of the Effect of Bovine Colostrum Against 5-FU-Induced Liver, Kidney, and Heart Toxicity in Rats
- PMID: 40283119
- PMCID: PMC12028551
- DOI: 10.3390/life15040564
Pathological Investigation of the Effect of Bovine Colostrum Against 5-FU-Induced Liver, Kidney, and Heart Toxicity in Rats
Abstract
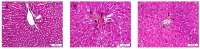
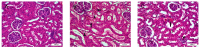
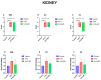
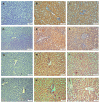
This study aimed to investigate the possible histopathological and immunohistochemical effects of bovine colostrum (BC) against the toxic effects of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) on the liver, kidney, and heart of Wistar Albino rats. Animals were divided into three groups: control, 5-FU, and 5-FU+BC. The control group received 2 mL/kg i.p. saline, the 5-FU group 100 mg/kg i.p. 5-FU, and the 5-FU+BC group received 100 mg/kg i.p. saline on the first day of the study. The 5-FU and 5-FU+BC groups received 100 mg/kg i.p. of 5-FU and 1000 mg/kg BC orally each day of the study. Liver, kidney, and heart tissues were examined histopathologically for lesions and the expression of TNF-α, HSP-27, CASP-3, and 8-OHdG. No pathologic lesions were observed in the control group, whereas severe pathologic lesions were observed in the 5-FU group. In the 5-FU+BC group, the lesions were less severe than in the 5-FU group. In immunohistochemical examination, biomarker expression was not observed in the control group, whereas it was severe in the 5-FU group and less severe in the 5-FU+BC group. At the end of the study, it was observed that 5-FU-induced pathological findings in liver, kidney, and heart tissues decreased with the use of bovine colostrum. The difference between the control group and the 5-FU and 5-FU+BC groups was significant (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05, respectively). Although the BC addition did not show any statistical significance in the pathological scores of 5-FU in liver, kidney, and heart tissues, it was observed that it improved the lesions of these tissues. Nevertheless, histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses showed visible improvements in the 5-FU+BC group. Although more studies are needed, it is hoped that BC will improve prognosis by both reducing the side effects of 5-FU, a good chemotherapeutic agent, and its antineoplastic properties.
Keywords: 5-FU; cancer; cardiotoxicity; hepatotoxicity; nephrotoxicity; pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



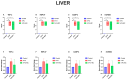
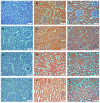



Similar articles
-
Effects of dexpanthenol on 5-fluorouraci-induced nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and intestinal mucositis in rats: a clinical, biochemical, and pathological study.Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2025 Feb 28;19(1):36-50. doi: 10.2478/abm-2025-0006. eCollection 2025 Feb. Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2025. PMID: 40231165 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects of naringin against 5-fluorouracil-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Apr;21(4):404-410. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2018.27510.6714. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29796225 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Kaempferol and Its Nanoparticles on 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Rats.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Feb 13;2022:2273000. doi: 10.1155/2022/2273000. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35198633 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of carvedilol alone and coadministered with diltiazem and prednisolone on doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2018 Feb;6(1):e00381. doi: 10.1002/prp2.381. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2018. PMID: 29417758 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of Ficus Carica extract and extra virgin olive oil against oxidative injury, cytokine liberation, and inflammation mediated by 5-Fluorouracil in cardiac and renal tissues of male albino rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Jan;28(4):4558-4572. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10778-0. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. Retraction in: Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Oct;31(49):59658. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-35285-4. PMID: 32946057 Retracted.
References
-
- Repici A., Capra A.P., Hasan A., Basilotta R., Scuderi S.A., Campolo M., Paterniti I., Esposito E., Ardizzone A. Ulva pertusa Modulated Colonic Oxidative Stress Markers and Clinical Parameters: A Potential Adjuvant Therapy to Manage Side Effects During 5-FU Regimen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024;25:12988. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312988. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

