Anatomical Considerations for Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection for Breast Augmentation in Young Female Patients
- PMID: 40283178
- PMCID: PMC12028494
- DOI: 10.3390/life15040624
Anatomical Considerations for Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection for Breast Augmentation in Young Female Patients
Abstract
Hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers offer a minimally invasive alternative for breast augmentation, appealing to young female patients seeking natural results and minimal recovery time. However, achieving optimal outcomes requires a thorough understanding of breast anatomy, filler properties, and safe injection techniques. This study provides a comprehensive analysis of the anatomical considerations, techniques, and filler properties necessary for optimal breast augmentation using HA filler. It also explores patient selection, long-term safety and efficacy, and the management of complications. A review of key anatomical structures, including glandular tissue, fascial layers, vascular anatomy, and Cooper's ligaments was conducted. Injection techniques, such as dual-plane and submuscular approaches, were analysed with a focus on pre-procedural imaging. Four cases of young female patients undergoing breast augmentation using HA filler (e.p.t.q. eve X, Jetema Inc., Seoul, Republic of Korea) were analysed. The efficacy of HA fillers in achieving natural breast enhancement was demonstrated in all four cases. Ultrasound played a crucial role in ensuring accurate filler placement, reducing risks like vascular occlusion and filler migration. Patients reported high satisfaction and minimal complications, though periodic treatments were required for maintenance. HA filler-based breast augmentation is a safe and effective option for young female patients, delivering natural results with rapid recovery. Although the results can be temporary and maintenance treatment is required, HA fillers may offer a non-invasive alternative to silicone implants. Optimal outcomes can be achieved through a thorough understanding of anatomy, the use of highly cohesive fillers, and ultrasound-guided injection techniques.
Keywords: anatomy; breast augmentation; cross-sectional; hyaluronic acid; injections; interventional; subcutaneous; ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Jovian Wan was employed by the company Medical Research Inc., Wonju, Korea. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
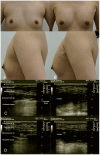
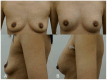
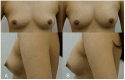
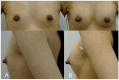
References
-
- Hidalgo D.A., Spector J.A. Breast augmentation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014;133:567–583. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

