Unexpectedly High and Difficult-to-Explain Regenerative Capacity in an 82-Year-Old Patient with Insulin-Requiring Type 2 Diabetes and End-Stage Renal Disease
- PMID: 40283387
- PMCID: PMC12027714
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14082556
Unexpectedly High and Difficult-to-Explain Regenerative Capacity in an 82-Year-Old Patient with Insulin-Requiring Type 2 Diabetes and End-Stage Renal Disease
Abstract
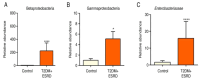
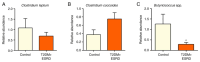
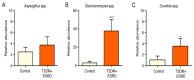
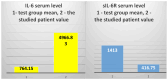
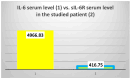
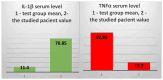
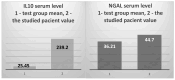
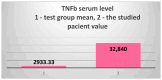
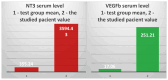
Background/Objectives: The case we present is part of a large study that we conducted on hemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and which set the following objectives: studying changes in the intestinal microbiota, innate and acquired immune response capacity, and tissue regeneration. Methods: (1) For the genetic study of the gut microbiota, special techniques that are not based on cultivation were used since most of the species in the intestinal flora are not cultivable. (2) The immunological study had two targets: innate immunity (inflammation) and adaptive immunity (we chose to address the cellular immune response because, unlike the humoral one, it is insufficiently studied in this category of associated pathologies). As markers for innate immunity (inflammation), the following were determined: IL-6, sIL-6R, IL-1β, TNFα, IL-10, and NGAL. TNFβ/LTα was determined as a marker for adaptive immunity (the cellular immune response). (3) The study of tissue regeneration capacity was performed using NT-3 (this is the first study to do so) and VEGFβ (another marker that is scarce in this category of patients) as markers. All the aforementioned compounds were determined from serum samples, utilizing Merck Millipore ELISA kits for IL-6, IL-1β, IL-10, NT-3, and VEGF β, and Elabscience ELISA kits for IL-6R, TNFα, TNFβ, and NGAL. Results: We were very surprised to find unexpected immunological changes and tissue regenerative capacity in one of the patients studied, an 82-year-old female patient diagnosed with insulin-dependent T2DM with multiple complications, including end-stage renal disease (ESRD). The patient showed a huge capacity for tissue regeneration, combined with amplification of immunological capacity, in comparison to patients in the same group (T2DM and ESRD) and to those in the control group (ESRD). Thus, extremely elevated serum concentrations of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-β, as well as the tissue regeneration indicators NT-3 and VEGFβ, were obtained in comparison to all other members of the patient group. At the same time, serum levels of the soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL6-R) and TNFα were greatly reduced compared to the test group's mean. Conclusions: All the data obtained during our research were corroborated with those from the specialized literature and entitle us to support the hypothesis that the cause of these unexpected behaviors is the genetically conditioned overproduction (possibly acquired post-infection) of IL-6, along with its predominant anti-inflammatory and pro-regenerative signaling through the membrane-bound receptor IL-6R.
Keywords: end-stage renal disease; inflammatory cytokines; neurotrophin-3; type 2 diabetes mellitus; vascular endothelial growth factor beta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 as a Director of Immunological Events and Tissue Regenerative Capacity in Hemodialyzed Diabetes Patients.Med Sci (Basel). 2024 Jun 15;12(2):31. doi: 10.3390/medsci12020031. Med Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921685 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
-
TNF-α and IL-1β Promote Renal Podocyte Injury in T2DM Rats by Decreasing Glomerular VEGF/eNOS Expression Levels and Altering Hemodynamic Parameters.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Dec 9;15:6657-6673. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S391473. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36532651 Free PMC article.
-
Whole blood production of monocytic cytokines (IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha, sIL-6R, IL-1Ra) in haemodialysed patients.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999 Oct;14(10):2420-6. doi: 10.1093/ndt/14.10.2420. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999. PMID: 10528667
-
Clinical efficacies, underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of Chinese medicines for diabetic nephropathy treatment and management.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Sep;11(9):2749-2767. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.020. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34589395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- New Global Kidney Health Report Sheds Light on Current Capacity Around the World to Deliver Kidney Care. [(accessed on 28 March 2025)]. Available online: https://www.theisn.org/blog/2023/03/30/new-global-kidney-health-report-s...
-
- Monardo P., Lacquaniti A., Campo S., Bucca M., Casuscelli di Tocco T., Rovito S., Ragusa A., Santoro A. Updates on hemodialysis techniques with a common denominator: The personalization of the dialytic therapy. Semin. Dial. 2021;34:183–195. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

