Sarcopenia Abdominal Muscle Mass Index Assessment Informs Surgical Decision-Making in Displaced Fractures of the Femoral Neck
- PMID: 40283403
- PMCID: PMC12027683
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14082573
Sarcopenia Abdominal Muscle Mass Index Assessment Informs Surgical Decision-Making in Displaced Fractures of the Femoral Neck
Abstract
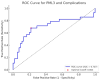
Background: Displaced femoral neck fractures (FNFs) can be treated with hemiarthroplasty (HA) or total hip arthroplasty (THA), with THA typically offered to fitter patients. Sarcopenia increases complications and mortality after hip arthroplasty. The psoas muscle-L3 vertebra ratio (PML3) is a sarcopenia marker. This study evaluated PML3's role in predicting postoperative outcomes and guiding surgical decision-making. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted at a single centre between January 2021 and December 2024. PML3 was measured on computed tomography (CT) at the L3 vertebra level for patients with displaced FNFs, comparing postoperative outcomes between HA and THA cohorts. Results: Eighty-three patients (fifty-seven female, twenty-six male) were analysed. Forty-three underwent THA, and forty underwent HA. Postoperative complications were higher in HA patients (48% vs. 21%, p = 0.019), with lower 30-day survival (90% vs. 98%). Median PML3 in the HA group was 0.70 mm2 (IQR: 0.47-1.47), lower than in the THA group (1.34 mm2, IQR: 1.00-1.78, p = 0.002). However, PML3 values for patients that suffered complications (irrespective of surgical decision) were essentially the same; HA, 0.57 mm2 (IQR: 0.43-1.83); THA 0.56 mm2 (IQR: 0.41-1.05, p = 0.847). ROC analysis showed PML3 as an acceptable predictor of postoperative complications, with an AUC of 0.71. Conclusions: Lower PML3 values correlate with higher postoperative complications and mortality following THA or HA for displaced FNFs, confirming its role as a prognostic marker. Some THA complications in low-PML3 patients might have been avoided by selecting less invasive HA, suggesting THA should be reserved for those with greater muscle reserves.
Keywords: fractures of the femoral neck; muscle mass; postoperative outcomes; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Baghdadi S., Kiyani M., Kalantar S.H., Shiri S., Sohrabi O., Beheshti Fard S., Afzal S., Khabiri S.S. Mortality Following Proximal Femoral Fractures in Elderly Patients: A Large Retrospective Cohort Study of Incidence and Risk Factors. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023;24:693. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06825-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Recommendations|Hip Fracture: Management|Guidance|NICE. [(accessed on 29 December 2024)]. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg124/chapter/recommendations#surgical-....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

