Proenkephalin 119-159 in Heart Failure: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Implications
- PMID: 40283487
- PMCID: PMC12027756
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14082657
Proenkephalin 119-159 in Heart Failure: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Implications
Abstract
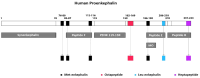
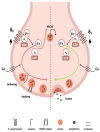
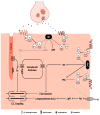
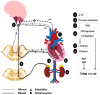
Heart failure (HF) is a challenging clinical syndrome with high morbidity and mortality rates. Along the spectrum of cardiovascular diseases, HF constitutes an ever-expanding area of research aiming at combating the associated mortality and improving the prognosis of patients with HF. Although natriuretic peptides have an established role among biomarkers in HF diagnosis and prognosis, several novel biomarkers reflecting the complex pathophysiology of HF are under investigation for their ability to predict adverse clinical outcomes in HF. Proenkephalin 119-159 (PENK119-159) is a non-functional peptide belonging to the enkephalin family of the endogenous opioid system and is considered a surrogate biomarker of the biologically active enkephalin peptides. PENK119-159 has demonstrated promising results in predicting short- and long-term mortality, readmission rates, and worsening renal function in patients with HF. Indeed, in the setting of HF, the levels of both active enkephalins and their surrogate PENK119-159 are elevated and are associated with a dismal prognosis. However, the biological effects of PENK119-159 remain largely unknown. Thus, it is crucial to gain a deeper insight into both the physiology of the enkephalin peptide family and the enkephalin-mediated cardiovascular regulation. In order to elucidate the complex pathophysiological mechanisms that lead to the upregulation of enkephalins in patients with HF, as well as the potential clinical implications of elevated enkephalins and PENK119-159 levels in this patient population, the present review will describe the physiology and distribution of the endogenous opioid peptides and their corresponding opioid receptors, with a particular focus on the action of enkephalins. The effects of the enkephalin peptides will be analyzed in both healthy subjects and patients with HF, especially with regard to their role in the regulation of cardiovascular and renal function. The review will also discuss the findings of recent studies that have explored the prognostic value of PENK119-159 in patients with HF.
Keywords: enkephalins; heart failure; opioid peptide receptors; pathophysiology; proenkephalin 119–159; worsening renal function.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest related to the work under consideration.
Figures
References
-
- Schulz C.-A., Christensson A., Ericson U., Almgren P., Hindy G., Nilsson P.M., Struck J., Bergmann A., Melander O., Orho-Melander M. High Level of Fasting Plasma Proenkephalin-A Predicts Deterioration of Kidney Function and Incidence of CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017;28:291–303. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015101177. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Treskatsch S., Feldheiser A., Shaqura M., Dehe L., Habazettl H., Röpke T.K., Shakibaei M., Schäfer M., Spies C.D., Mousa S.A. Cellular Localization and Adaptive Changes of the Cardiac Delta Opioid Receptor System in an Experimental Model of Heart Failure in Rats. Heart Vessels. 2016;31:241–250. doi: 10.1007/s00380-014-0620-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

