Artificial Intelligence in Thoracic Surgery: A Review Bridging Innovation and Clinical Practice for the Next Generation of Surgical Care
- PMID: 40283559
- PMCID: PMC12027631
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14082729
Artificial Intelligence in Thoracic Surgery: A Review Bridging Innovation and Clinical Practice for the Next Generation of Surgical Care
Abstract
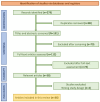
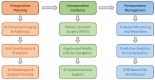
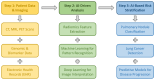
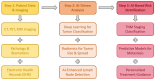
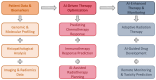
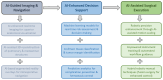
Background: Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming thoracic surgery by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, surgical precision, intraoperative guidance, and postoperative management. AI-driven technologies, including machine learning (ML), deep learning, computer vision, and robotic-assisted surgery, have the potential to optimize clinical workflows and improve patient outcomes. However, challenges such as data integration, ethical concerns, and regulatory barriers must be addressed to ensure AI's safe and effective implementation. This review aims to analyze the current applications, benefits, limitations, and future directions of AI in thoracic surgery. Methods: This review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. A comprehensive literature search was performed using PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library for studies published up to January 2025. Relevant articles were selected based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, focusing on AI applications in thoracic surgery, including diagnostics, robotic-assisted surgery, intraoperative guidance, and postoperative care. A risk of bias assessment was conducted using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool and ROBINS-I for non-randomized studies. Results: Out of 279 identified studies, 36 met the inclusion criteria for qualitative synthesis, highlighting AI's growing role in diagnostic accuracy, surgical precision, intraoperative guidance, and postoperative care in thoracic surgery. AI-driven imaging analysis and radiomics have improved pulmonary nodule detection, lung cancer classification, and lymph node metastasis prediction, while robotic-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS) has enhanced surgical accuracy, reduced operative times, and improved recovery rates. Intraoperatively, AI-powered image-guided navigation, augmented reality (AR), and real-time decision-support systems have optimized surgical planning and safety. Postoperatively, AI-driven predictive models and wearable monitoring devices have enabled early complication detection and improved patient follow-up. However, challenges remain, including algorithmic biases, a lack of multicenter validation, high implementation costs, and ethical concerns regarding data security and clinical accountability. Despite these limitations, AI has shown significant potential to enhance surgical outcomes, requiring further research and standardized validation for widespread adoption. Conclusions: AI is poised to revolutionize thoracic surgery by enhancing decision-making, improving patient outcomes, and optimizing surgical workflows. However, widespread adoption requires addressing key limitations through multicenter validation studies, standardized AI frameworks, and ethical AI governance. Future research should focus on digital twin technology, federated learning, and explainable AI (XAI) to improve AI interpretability, reliability, and accessibility. With continued advancements and responsible integration, AI will play a pivotal role in shaping the next generation of precision thoracic surgery.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; digital twin; explainable AI (XAI); intraoperative guidance; machine learning; postoperative care; radiomics; robotic-assisted surgery; surgical innovation; thoracic surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial Intelligence in Cardiac Surgery: Transforming Outcomes and Shaping the Future.Clin Pract. 2025 Jan 14;15(1):17. doi: 10.3390/clinpract15010017. Clin Pract. 2025. PMID: 39851800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Aesthetic Medicine: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Jun;24(6):e70241. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70241. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40501296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The integration of artificial intelligence into clinical medicine: Trends, challenges, and future directions.Dis Mon. 2025 Jun;71(6):101882. doi: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2025.101882. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Dis Mon. 2025. PMID: 40140300
-
Artificial intelligence (AI) in restorative dentistry: current trends and future prospects.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Apr 18;25(1):592. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05989-1. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40251567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive overview of artificial intelligence in surgery: a systematic review and perspectives.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Apr;477(4):617-626. doi: 10.1007/s00424-025-03076-6. Epub 2025 Mar 15. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 40087157
Cited by
-
Lung parenchymal trauma biomechanics, mechanisms, and classification: a narrative review of the current knowledge.Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2025 Jun 18;22(2):100-111. doi: 10.5114/kitp.2025.152221. eCollection 2025 Jun. Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2025. PMID: 40718668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

