Evaluation of the Decrease in DPOAE Levels After VEMP Testing in Clinical Patients Referred to the Vertigo Outpatient Clinic
- PMID: 40283595
- PMCID: PMC12027711
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14082766
Evaluation of the Decrease in DPOAE Levels After VEMP Testing in Clinical Patients Referred to the Vertigo Outpatient Clinic
Abstract
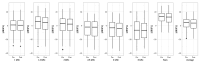
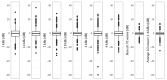
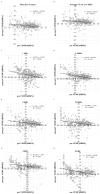
Background/Objectives: The objective of this study is to determine whether the strong acoustic stimuli used in vestibular evoked myogenic potential (VEMP) testing contribute to distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) level reduction due to noise-induced hearing loss. Methods: The DPOAE levels were measured routinely to evaluate vestibular balance disorders with sensorineural hearing loss and to monitor changes in cochlear function before and after VEMP. The changes in DPOAE levels after VEMP testing in 174 patients (80 males and 94 females; median age, 53 years [interquartile range, 39-67 years; range, 15-85 years]) who were examined in the vertigo outpatient clinic between June 2021 and December 2024 were retrospectively analyzed. Results: The DPOAE levels decreased significantly after VEMP testing at 1.4 kHz, 2 kHz, 2.8 kHz, sum all 1/2 octave, and average 1/2 octave (1-6 kHz). The decrease in DPOAE levels at 6 kHz exhibited a significant negative linear correlation with age (the coefficient of determination: 0.0189, p = 0.01), but not sex or side. Conclusions: The strong sound stimulation used in VEMP testing can decrease DPOAE levels. The frequencies at which DPOAE levels decreased significantly were overtones of the stimulus frequency, suggesting a possible effect of acoustic stimulation. VEMP testing can be an invasive test method and should be performed with detailed consideration of the risks and benefits. The age factor can influence the decrease in DPOAE levels in VEMP testing.
Keywords: DPOAE; NIHL; SNHL; VEMP; noise-induced hearing loss; sensorineural hearing loss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Changes in cochlear function related to acoustic stimulation of cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential stimulation.Hear Res. 2016 Oct;340:43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2015.12.022. Epub 2015 Dec 25. Hear Res. 2016. PMID: 26724755
-
Air-Conducted Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential Testing in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults: Thresholds, Frequency Tuning, and Effects of Sound Exposure.Ear Hear. 2019 Jan/Feb;40(1):192-203. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000607. Ear Hear. 2019. PMID: 29870520 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of High Sound Exposure During Air-Conducted Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential Testing in Children and Young Adults.Ear Hear. 2018 Mar/Apr;39(2):269-277. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000484. Ear Hear. 2018. PMID: 29466264 Free PMC article.
-
Safe Use of Acoustic Vestibular-Evoked Myogenic Potential Stimuli: Protocol and Patient-Specific Considerations.J Am Acad Audiol. 2017 Sep;28(8):708-717. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.16071. J Am Acad Audiol. 2017. PMID: 28906242 Review.
-
A review of the effectiveness of otoacoustic emissions for evaluating hearing status after newborn screening.Otol Neurotol. 2013 Aug;34(6):1058-63. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e318282964f. Otol Neurotol. 2013. PMID: 23628790 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

