Current Role of the Nonsteroid Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (ISSNHL): A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40283640
- PMCID: PMC12028189
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14082811
Current Role of the Nonsteroid Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (ISSNHL): A Narrative Review
Abstract
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHNL) is an abruptly appearing hearing loss. The etiology remains unclear, although vascular pathologies, viral infections, or autoimmune disease contribute to the understanding of this pathology. Systematic steroids are often used as the first-line treatment because of their anti-inflammatory effect. However, there remains controversy about the use of steroids and other alternative treatments, as hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), exploratory tympanotomy, prostaglandin, N-acetylcysteine, or defibrinogenation therapy. In this study, we aim to review the various treatment options currently available for sudden hearing loss, with the objective of advancing our understanding of this condition and clarifying information to guide future clinical practice guidelines.
Keywords: exploratory tympanotomy; hyperbaric oxygen therapy; nonsteroid treatment; prostaglandin; sudden sensorineural hearing loss; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
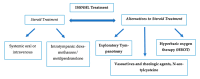


References
-
- Herrera M., García-Berrocal J.R., García-Arumi A., Lavilla M.J., Plaza G., Grupo de Trabajo de la Comisión de Audiología de la SEORL Update on consensus on diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2019;70:290–300. doi: 10.1016/j.otorri.2018.04.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chandrasekhar S.S., Tsai-Do B.S., Schwartz S.R., Bontempo L.J., Faucett E.A., Finestone S.A., Hollingsworth D.B., Kelley D.M., Kmucha S.T., Moonis G., et al. Clinical practice guideline: Sudden hearing loss (update) Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019;161:S1–S45. doi: 10.1177/0194599819859885. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

