Long-Term Performance and Safety of the Self-Expandable Carotid Stent MER: 5-Year Outcomes from the OCEANUS Study, with Subgroup Analysis Based on Predilatation Before Carotid Artery Stenting
- PMID: 40283644
- PMCID: PMC12027988
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14082814
Long-Term Performance and Safety of the Self-Expandable Carotid Stent MER: 5-Year Outcomes from the OCEANUS Study, with Subgroup Analysis Based on Predilatation Before Carotid Artery Stenting
Abstract
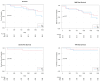
Background: Carotid artery stenting (CAS) with neuroprotection is a widely used treatment for carotid artery stenosis. This study aimed to evaluate the long-term outcomes of CAS using the MER stent (Balton, Poland) and various neuroprotection devices, with subgroup analysis based on predilatation. Methods: A prospective analysis was conducted on patients treated with CAS at four high-volume centers in Poland between October 2016 and May 2017. Patients were stratified into two groups based on whether predilatation was performed. Procedural and clinical outcomes, including major adverse events (MAEs) defined as all-cause death, stroke, and myocardial infarction (MI), were evaluated at 30 days and 5 years post-procedure. Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regression models were used to assess event-free survival and predictors of MAEs. Results: The study population consisted of 100 patients (males: 61%) with a mean age of 68 years. Dyslipidemia (84.4% vs. 60.0%, p = 0.007) and smoking (67.3% vs. 44.4%, p = 0.022) differed significantly between the predilatation and non-predilatation groups. The procedural success rate (<30% residual stenosis) was 97%. At 5 years, the overall restenosis rate was 7%, and target vessel revascularization was required in 3% of patients. The cumulative mortality rate was 15%, and two strokes (2%) were recorded. Multivariable regression identified prior CABG as an independent predictor of MAEs (HR 3.5, 95% CI 1.14-10.83, p = 0.03). Conclusions: CAS with the MER stent demonstrated high procedural success and favorable long-term outcomes. Predilatation did not impact outcomes. Neuroprotection was effective in all cases, with no device-related complications reported.
Keywords: MER stent; Robin; carotid artery stenting; long-term outcomes; major adverse events; neuroprotection; predilatation; restenosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors received fees from the sponsor (Balton, Warsaw, Poland).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct coronary stent implantation does not reduce the incidence of in-stent restenosis or major adverse cardiac events: six month results of a randomized trial.Eur Heart J. 2003 Mar;24(5):421-9. doi: 10.1016/s0195-668x(02)00701-7. Eur Heart J. 2003. PMID: 12633544 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term Comparative Outcomes of Carotid Artery Stenting Following Previous Carotid Endarterectomy vs De Novo Lesions.J Endovasc Ther. 2015 Jun;22(3):449-56. doi: 10.1177/1526602815581597. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Endovasc Ther. 2015. PMID: 25878023 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Factors for Neurologic Outcome in Patients with Carotid Artery Stenting.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2016 Mar;32(2):205-14. doi: 10.6515/acs20150119h. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2016. PMID: 27122951 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of contralateral carotid artery occlusions on short- and long-term outcomes of carotid artery stenting: a retrospective single-center analysis and review of literature.Int Angiol. 2021 Apr;40(2):87-96. doi: 10.23736/S0392-9590.20.04525-3. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Int Angiol. 2021. PMID: 33274909 Review.
-
A meta-analysis of the effect of stent design on clinical and radiologic outcomes of carotid artery stenting.J Vasc Surg. 2019 Jun;69(6):1952-1961.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.11.017. J Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 31159989
References
-
- Prendes C.F., Rantner B., Hamwi T., Stana J., Feigin V.L., Stavroulakis K., Tsilimparis N., on behalf of the GBD Collaborators Study Group Burden of Stroke in Europe: An Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study Findings From 2010 to 2019. Stroke. 2024;55:432–442. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.042022. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous