New Interleukin-23 Antagonists' Use in Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 40283885
- PMCID: PMC12030181
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18040447
New Interleukin-23 Antagonists' Use in Crohn's Disease
Abstract
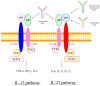
Crohn's disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the digestive tract, driven by an imbalance in immune system regulation, where proinflammatory interleukin-23 (IL-23) plays an essential role. Selective new IL-23 inhibitors, including risankizumab, guselkumab, and mirikizumab, block the IL-23p19 subunit to inhibit the Il-23 action and alleviate inflammation in CD. This review explores the effectiveness, safety, and therapeutic potential of anti-IL-23 treatment in CD management. Risankizumab, guselkumab, and mirikizumab demonstrated considerable effectiveness in inducing clinical remission and promoting endoscopic healing in patients with moderately to severely active CD, including those refractory to anti-TNF therapies. Risankizumab showed favorable results in pivotal trials like ADVANCE, MOTIVATE, and FORTIFY, achieving remission rates of up to 45% and sustained inflammatory biomarkers normalization. Guselkumab and mirikizumab similarly demonstrated substantial efficacy in the induction and maintenance phases, with promising long-term results. The safety profiles of IL-23 inhibitors were favorable, with low rates of serious adverse events, including infections and malignancies. Selective new IL-23 inhibitors represent a targeted and effective therapeutic class for moderately to severely active CD, offering high clinical and endoscopic remission rates, and favorable safety outcomes. Continued research, particularly on long-term efficacy and the selection of patients based on inflammatory biomarkers, will help optimize their role in personalized treatment strategies for refractory CD.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; IL-23 inhibitors; guselkumab; inflammatory bowel disease; mirikizumab; risankizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Estevinho M.M., Cabeda J., Santiago M., Machado E., Silva R., Duro M., Pita I., Morais R., Macedo G., Bull T.J., et al. Viable Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis Colonizes Peripheral Blood of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients. Microorganisms. 2023;11:1520. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061520. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources