Preparation and Evaluation of Hepatoma-Targeting Glycyrrhetinic Acid Composite Micelles Loaded with Curcumin
- PMID: 40283886
- PMCID: PMC12030034
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18040448
Preparation and Evaluation of Hepatoma-Targeting Glycyrrhetinic Acid Composite Micelles Loaded with Curcumin
Abstract
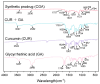
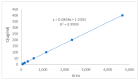
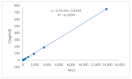
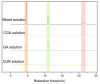
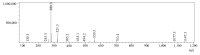
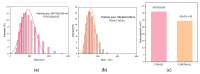
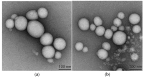
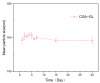
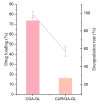
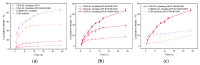
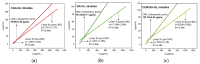
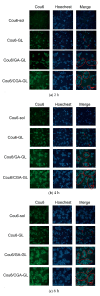
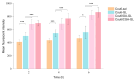
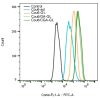
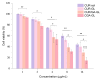
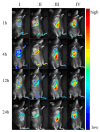
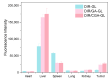
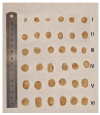
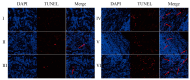
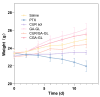
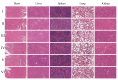
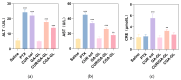
Background: Liver cancer, especially hepatocellular carcinoma, a prevalent malignant tumor of the digestive system, poses significant therapeutic challenges. While traditional chemotherapy can inhibit tumor progression, its clinical application is limited by insufficient efficacy. Hydrophobic therapeutic agents further encounter challenges including low tumor specificity, poor bioavailability, and severe systemic toxicity. This study aimed to develop a liver-targeted, glutathione (GSH)-responsive micellar system to synergistically enhance drug delivery and antitumor efficacy. Methods: A GSH-responsive disulfide bond was chemically synthesized to conjugate glycyrrhetinic acid (GA) with curcumin (Cur) at a molar ratio of 1:1, forming a prodrug Cur-GA (CGA). This prodrug was co-assembled with glycyrrhizic acid (GL) at a 300% w/w loading ratio into micelles. The system was characterized for physicochemical properties, in vitro drug release in PBS (7.4) without GSH and in PBS (5.0) with 0, 5, or 10 mM GSH, cellular uptake in HepG2 cells, and in vivo efficacy in H22 hepatoma-bearing BALB/c mice. Results: The optimized micelles exhibited a hydrodynamic diameter of 157.67 ± 2.14 nm (PDI: 0.20 ± 0.02) and spherical morphology under TEM. The concentration of CUR in micelles can reach 1.04 mg/mL. In vitro release profiles confirmed GSH-dependent drug release, with 67.5% vs. <40% cumulative Cur release observed at 24 h with/without 10 mM GSH. Flow cytometry and high-content imaging revealed 1.8-fold higher cellular uptake of CGA-GL micelles compared to free drug (p < 0.001). In vivo, CGA-GL micelles achieving 3.6-fold higher tumor accumulation than non-targeted controls (p < 0.001), leading to 58.7% tumor volume reduction (p < 0.001). Conclusions: The GA/GL-based micellar system synergistically enhanced efficacy through active targeting and stimuli-responsive release, providing a promising approach to overcome current limitations in hydrophobic drug delivery for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.
Keywords: glycyrrhetinic acid; glycyrrhizic acid; liver cancer; micelles; target delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hepatoma-Targeting and ROS-Responsive Polymeric Micelle-Based Chemotherapy Combined with Photodynamic Therapy for Hepatoma Treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Sep 16;19:9613-9635. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S475531. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39309184 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of novel reduction-sensitive hybrid nano-echinus-like nanomedicine.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup2):659-667. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2018.1466147. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29703084
-
Glycyrrhetinic acid-decorated and reduction-sensitive micelles to enhance the bioavailability and anti-hepatocellular carcinoma efficacy of tanshinone IIA.Biomater Sci. 2016 Jan;4(1):167-82. doi: 10.1039/c5bm00224a. Biomater Sci. 2016. PMID: 26484363
-
Folic acid-targeted disulfide-based cross-linking micelle for enhanced drug encapsulation stability and site-specific drug delivery against tumors.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Mar 18;11:1119-30. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S101649. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27051287 Free PMC article.
-
Glycyrrhizic acid-based multifunctional nanoplatform for tumor microenvironment regulation.Chin J Nat Med. 2024 Dec;22(12):1089-1099. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(24)60685-0. Chin J Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 39725510 Review.
References
-
- Devarbhavi H.C., Asrani S.K., Arab J.P., Nartey Y.A., Pose E., Kamath P.S. Global burden of Liver Disease: 2023 Update. J. Hepatol. 2023;79:516–537. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

