Hypoxia Imaging in Lung Cancer: A PET-Based Narrative Review for Clinicians and Researchers
- PMID: 40283896
- PMCID: PMC12030053
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18040459
Hypoxia Imaging in Lung Cancer: A PET-Based Narrative Review for Clinicians and Researchers
Abstract
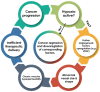
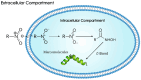
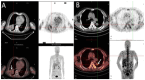
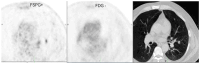
Background: Hypoxia plays a critical role in lung cancer progression and treatment resistance by contributing to aggressive tumor behavior and poor therapeutic response. Molecular imaging, particularly positron emission tomography (PET), has become an essential tool for noninvasive hypoxia detection, providing valuable insights into tumor biology and aiding in personalized treatment strategies. Objective: This narrative review explores recent advancements in PET imaging for detecting hypoxia in lung cancer, with a focus on the development, characteristics, and clinical applications of various radiotracers. Findings: Numerous PET-based hypoxia radiotracers have been investigated, each with distinct pharmacokinetics and imaging capabilities. Established tracers such as 18F-Fluoromisonidazole (18F-FMISO) remain widely used, while newer alternatives like 18F-Fluoroazomycin Arabinoside (18F-FAZA) and 18F-Flortanidazole (18F-HX4) demonstrate improved clearance and image contrast. Additionally, 64Cu-ATSM has gained attention for its rapid tumor uptake and hypoxia selectivity. The integration of PET with hybrid imaging modalities, such as PET/CT and PET/MRI, enhances the spatial resolution and functional interpretation, making hypoxia imaging a promising approach for guiding radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies. Conclusions: PET imaging of hypoxia offers significant potential in lung cancer diagnosis, treatment planning, and therapeutic response assessment. However, challenges remain, including tracer specificity, quantification variability, and standardization of imaging protocols. Future research should focus on developing next-generation radiotracers with enhanced specificity, optimizing imaging methodologies, and leveraging multimodal approaches to improve clinical utility and patient outcomes.
Keywords: cancer; emission; hypoxia; positron; tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
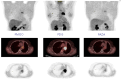
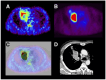
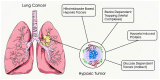
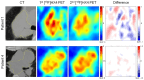
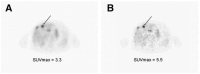
References
-
- National Cancer Institute Lung and Bronchus Cancer; Cancer Stat Facts. [(accessed on 14 April 2024)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/lungb.html.
-
- Oprea-Lager D.E., MacLennan S., Bjartell A., Briganti A., Burger I.A., de Jong I., De Santis M., Eberlein U., Emmett L., Fizazi K., et al. European association of nuclear medicine focus 5: Consensus on molecular imaging and theranostics in prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2024;85:49–60. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.09.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: New dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

