Enhancing Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) with Materials Based on COSAN-Functionalized Nanoparticles
- PMID: 40283902
- PMCID: PMC12030506
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18040466
Enhancing Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) with Materials Based on COSAN-Functionalized Nanoparticles
Abstract
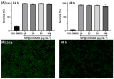
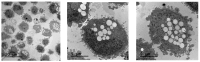
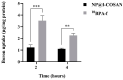
Background/Objectives: Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is a promising approach for selectively targeting and destroying malignant cells using 10B isotopes. A significant challenge in BNCT lies in the development of efficient boron delivery systems that ensure adequate boron accumulation within tumor cells. This study aims to synthesize, characterize, and evaluate COSAN-functionalized nanoparticles (NP@I-COSAN) as a potential boron carrier for BNCT. Methods: Hybrid nanoparticles were synthesized by conjugating monoiodinated cobaltabisdicarbollides (I-COSAN) to commercially available acrylic polymer-based nanoparticles. Functionalization and cellular uptake were confirmed through FTIR, TGA, UV-Vis spectroscopy, and TEM/EDX analyses. Biocompatibility was evaluated by assessing cytotoxicity in HeLa cells and C. elegans as an in vivo model. Intracellular boron uptake was quantified using ICP-MS, with results compared to those obtained with 4-borono-L-phenylalanine conjugated to fructose (f-BPA). An in vitro BNCT proof-of-concept assay was also performed to evaluate therapeutic efficacy. Results: NP@I-COSAN demonstrated low cytotoxicity and efficient internalization in cells. ICP-MS analysis revealed stable boron retention, comparable to traditional boron agents. The BNCT assay further showed that NP@I-COSAN was effective in inducing tumor cell apoptosis, even at lower boron concentrations than conventional treatments. Conclusions: These results underscore the potential of NP@I-COSAN as an effective boron delivery system for BNCT, offering a promising strategy to enhance boron accumulation within tumor cells and improve treatment efficacy.
Keywords: BNCT; C. elegans; boron clusters; metallacarboranes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
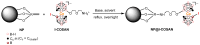

References
-
- Al-Thani A.N., Jan A.G., Abbas M., Geetha M., Sadasivuni K.K. Nanoparticles in cancer theragnostic and drug delivery: A comprehensive review. Life Sci. 2024;352:122899. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- PID2022-136892NB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- PID2021-122645OB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- CEX2019-000917/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- CEX2023-001263-S/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- 2021-SGR-00442/Government of Catalonia
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

