Endoplasmic Reticulum-Targeted Phototherapy Remodels the Tumor Immunopeptidome to Enhance Immunogenic Cell Death and Adaptive Anti-Tumor Immunity
- PMID: 40283929
- PMCID: PMC12030737
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18040491
Endoplasmic Reticulum-Targeted Phototherapy Remodels the Tumor Immunopeptidome to Enhance Immunogenic Cell Death and Adaptive Anti-Tumor Immunity
Abstract
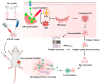
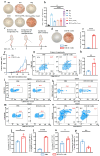
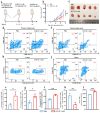
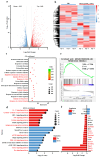
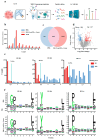
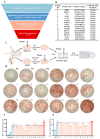
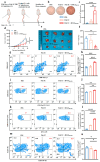
Background: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-targeted phototherapy has emerged as a promising approach to amplify ER stress, induce immunogenic cell death (ICD), and enhance anti-tumor immunity. However, its impact on the antigenicity of dying tumor cells remains poorly understood. Methods: Laser activation of the ER-targeted photosensitizer ER-Cy-poNO2 was performed to investigate its effects on tumor cell antigenicity. Transcriptomic analysis was carried out to assess gene expression changes. Immunopeptidomics profiling was used to identify high-affinity major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) ligands. In vitro functional studies were conducted to evaluate dendritic cell maturation and T lymphocyte activation, while in vivo experiments were performed by combining the identified peptide with poly IC to evaluate anti-tumor immunity. Results: Laser activation of ER-Cy-poNO2 significantly remodeled the antigenic landscape of 4T-1 tumor cells, enhancing their immunogenicity. Transcriptomic analysis revealed upregulation of antigen processing and presentation pathways. Immunopeptidomics profiling identified multiple high-affinity MHC-I ligands, with IF4G3986-994 (QGPKTIEQI) showing exceptional immunogenicity. In vitro, IF4G3986-994 promoted dendritic cell maturation and enhanced T lymphocytes activation. In vivo, the combination of IF4G3986-994 with poly IC elicited robust anti-tumor immunity, characterized by increased CD8+ T lymphocytes infiltration, reduced regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the tumor microenvironment, elevated systemic Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) levels, and significant tumor growth inhibition without systemic toxicity. Conclusions: These findings establish a mechanistic link between ER stress-driven ICD, immunopeptidome remodeling, and adaptive immune activation, highlighting the potential of ER-targeted phototherapy as a platform for identifying immunogenic peptides and advancing peptide-based cancer vaccines.
Keywords: ER-targeted phototherapy; adaptive anti-tumor immunity; endoplasmic reticulum stress; immunogenic cell death; immunogenic peptides; tumor immunopeptidome remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yuan X., Zhou J.-L., Yuan L., Fan J., Yoon J., Zhang X.-B., Peng X., Tan W. Phototherapy: Progress, challenges, and opportunities. Sci. China Chem. 2024;68:865. doi: 10.1007/s11426-024-2411-7. - DOI
-
- Sun Z., Zhao M., Wang W., Hong L., Wu Z., Luo G., Lu S., Tang Y., Li J., Wang J., et al. 5-ALA mediated photodynamic therapy with combined treatment improves anti-tumor efficacy of immunotherapy through boosting immunogenic cell death. Cancer Lett. 2023;554:216032. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.216032. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX1072/Chongqing Natural Science Foundation
- CSTB2022TFII-0IX0077/Chongqing Technology Foresight and System Innovation Project
- YKCSZ23057/Chongqing Graduate Education Curriculum Ideological and Political Demonstration Project
- ZXYZZKY02/Talent Innovation Ability Training Program of Army Medical Center
- GZC20233600/Postdoctoral Research Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

