Modulation of the Main Resistance-Associated ABC Transporter's Expression by Plant Flavonol Isorhamnetin
- PMID: 40283931
- PMCID: PMC12029997
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18040494
Modulation of the Main Resistance-Associated ABC Transporter's Expression by Plant Flavonol Isorhamnetin
Abstract
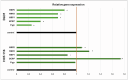
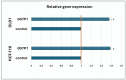
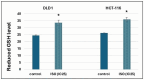
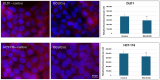
Background/Objectives: Multidrug resistance is one the leading problems in cancer treatment, where the overexpression of P-gp and other drug efflux pumps is regarded as the primary cause. With the intention to develop transporter inhibitors, natural products such as phenolics have shown great potential and diverse attention recently. Among these, isorhamnetin (ISO), an O-methylated flavonol, is predominantly found in the fruits and leaves of various plants. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the effects of ISO on the mRNA expression of membrane transporters P-gp, BCRP, MRP 1, 2, and 5, the protein expression of P-gp, as well as the GSTP1 and GSH content in DLD1 and HCT-116 colon cancer cells. Methods: The cytotoxic effect of isorhamnetin is assessed using an MTT test, while qPCR and immunocytochemistry methods were used to determine gene and protein expression levels. The concentration of reduced glutathione was determined using the colorimetric method. Results: Based on the results, ISO can modulate the expression of transporters responsible for the resistance development (all transporters on the transcriptional level were downregulated in DLD1 cells, while only MRP1 on HCT-116 cells, and reduced P-gp protein expression on both investigated cell lines). Increased glutathione content in treated cells and GSTP1 expression suggest metabolizing the ISO and potential ejection with GSH-dependent pumps. Conclusions: Thus, in future experiments, ISO as a natural medicinal compound could be used as a chemosensitizer to prevent or overcome membrane transporter-mediated drug resistance.
Keywords: BCRP; MDR; MRPs; P-gp; cancer cell resistance; isorhamnetin.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reversal of multidrug resistance by Marsdenia tenacissima and its main active ingredients polyoxypregnanes.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 May 5;203:110-119. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.03.051. Epub 2017 Mar 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28363522
-
5-Oxo-hexahydroquinoline derivatives as modulators of P-gp, MRP1 and BCRP transporters to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 1;362:136-149. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.10.025. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30391378
-
Modulation of function of three ABC drug transporters, P-glycoprotein (ABCB1), mitoxantrone resistance protein (ABCG2) and multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCC1) by tetrahydrocurcumin, a major metabolite of curcumin.Mol Cell Biochem. 2007 Feb;296(1-2):85-95. doi: 10.1007/s11010-006-9302-8. Epub 2006 Sep 8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 16960658
-
Overcoming Multidrug Resistance: Flavonoid and Terpenoid Nitrogen-Containing Derivatives as ABC Transporter Modulators.Molecules. 2020 Jul 24;25(15):3364. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153364. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32722234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transporter-mediated multidrug resistance and its modulation by Chinese medicines and other herbal products.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2010 Mar;7(1):54-66. doi: 10.2174/157016310791162712. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2010. PMID: 20156136 Review.
Cited by
-
Isorhamnetin Modulates Drug-Resistance-Related Biomarkers in Colon Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 27;26(13):6208. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136208. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gillet J.P., Gottesman M.M. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010;596:47–76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

