Recent Developments of 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Compounds as Anticancer Agents
- PMID: 40284015
- PMCID: PMC12030488
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18040580
Recent Developments of 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Compounds as Anticancer Agents
Abstract
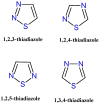
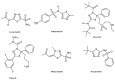
The World Health Organization has recently underlined the increasing global burden of cancer, with a particularly alarming impact on underserved populations. In recent years, 1,3,4-thiadiazole has emerged as a versatile pharmacophore to obtain bioactive compounds. The pharmacological properties of this ring are primarily attributed to its role as a bioisostere of pyrimidine, the core structure of three nucleic bases. This structural feature endows 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives with the ability to interfere with DNA replication processes. Additionally, the mesoionic behavior of this heterocycle gives it important properties, such as the ability to cross biological membranes and interact with target proteins. Noteworthy, in analogy to the other sulfur heterocycles, the presence of C-S σ* orbitals, conferring small regions of low electron density on the sulfur atom, makes interaction with the target easier. This review focuses on the most promising anticancer agents with 1,3,4-thiadiazole structure reported in the past five years, providing information that may be useful to medicinal chemists who intend to develop new anticancer derivatives.
Keywords: 1,3,4-thiadiazoles; anticancer agents; breast cancer; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; sulfur-containing heterocycles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
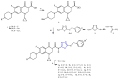
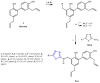
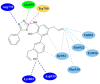
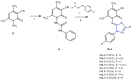
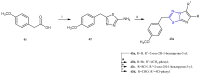
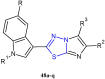

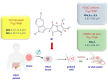
References
-
- Meanwell N.A. Chapter Five—A Synopsis of the Properties and Applications of Heteroaromatic Rings in Medicinal Chemistry. In: Scriven E.F.V., Ramsden C.A., editors. Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry. Volume 123. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2017. pp. 245–361.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

