Exploring the Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Disabled Saudi Patients: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40284017
- PMCID: PMC12030500
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18040582
Exploring the Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Disabled Saudi Patients: A Systematic Review
Abstract
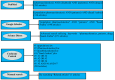
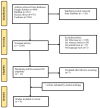
Background/Objectives: Disability is a term that involves mental, intellectual, or sensory impairment resulting in the loss of one's ability to walk or perform the activities necessary to live in a society. This study aims to collect all the data regarding the absorption, distribution, and disposition of drugs in disabled Saudi patients, i.e., patients suffering from epilepsy, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, etc., and then compare these results with data reported in other ethnicities. Methods: An exhaustive online search used the key terms in Google Scholar, PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Science Direct to extract all articles that met the eligibility criteria. All research studies containing pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters (area under the curve from 0 to infinity (AUC0-∞), maximal plasma concentration (Cmax), clearance (CL), volume of distribution, time to reach maximum plasma concentration, and half-life) were included in this review. Results: In pediatric epileptic patients, carbamazepine showed a notable decrease in Cmax with increasing age, which may be due to ontogenetic changes in its disposition. The AUC0-∞ of busulphan in adult hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients was recorded as 4392.5 ± 1354.65 μg·h/mL, with high inter-individual variability. Moreover, the CL of vancomycin was reported to be 25% higher among cancer patients in comparison to non-cancer subjects. Conclusions: The complications in disabled patients due to alterations in cytochrome P450 enzymes, pathophysiology, genetics, and ethnicity emphasize the significance of patient-centered drug dosing. These findings may aid healthcare physicians in refining therapeutic care in this population.
Keywords: Saudi Arabia; absorption; cancer; clearance; disposition; drugs; epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) [(accessed on 8 December 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/classifications/international-classification-of-func....
-
- Definition of Disability. [(accessed on 8 November 2024)]. Available online: https://www.dundee.ac.uk/corporate-information/definition-disability.
-
- Hedaya M.A. Basic Pharmacokinetics. Routledge; London, UK: 2023.
-
- Awofisayo S.O., Akpabio A., Olorunsola E.O., Arhewoh M.I. Lifestyle Biopharmaceutics and Mechanistic Basis of Drug Clinical Outcomes: A Review. J. Adv. Pharm. Res. 2024;8:63–76. doi: 10.21608/aprh.2024.257304.1245. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous