Synthesis and Neurotropic Activity of New 5-Piperazinopyrazolo[3,4- c]-2,7-naphthyridines and Isoxazolo[5,4- c]-2,7-naphthyridines
- PMID: 40284032
- PMCID: PMC12030261
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18040597
Synthesis and Neurotropic Activity of New 5-Piperazinopyrazolo[3,4- c]-2,7-naphthyridines and Isoxazolo[5,4- c]-2,7-naphthyridines
Abstract
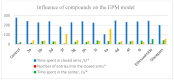
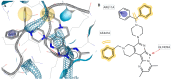
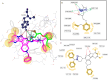
Background/Objectives: Approximately 1% of people worldwide suffer from epilepsy. The development of safer and more effective antiepileptic medications (AEDs) is still urgently needed because all AEDs have some unwanted side effects and roughly 30% of epileptic patients cannot stop having seizures when taking current AEDs. It should be noted that the derivatives of pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine are important core structures in many drug substances. The aim of this study is to synthesize new derivatives of piperazino-substituted pyrazolo[3,4-c]-2,7-naphthyridines and 9,11-dimethylpyrimido[1',2':1,5]pyrazolo[3,4-c]-2,7-naphthyridines for the evaluation of their neurotropic activity. Methods: The synthesis of the target compounds was performed starting from 1-amino-3-chloro-2,7-naphthyridines and using well-known methods. The structures of all the synthesized compounds were confirmed by spectroscopic data. Compounds were studied for their potential neurotropic activities (anticonvulsant, sedative, anti-anxiety, and antidepressive), as well as side effects, in 450 white mice of both sexes and 50 male Wistar rats. The anticonvulsant effect of the newly synthesized compounds was investigated by using the following tests: pentylenetetrazole, thiosemicarbazide-induced convulsions, and maximal electroshock. The psychotropic properties of the selected compounds were evaluated by using the following tests: the Open Field test, the Elevated Plus Maze (EPM), the Forced Swimming test, and Rotating Rod Test to study muscle relaxation. For the docking studies, AutoDock 4 (version 4.2.6) was used, as well as the structures of the GABAA receptor (PDB ID: 4COF), the SERT transporter (PDB ID: 3F3A), and the 5-HT1A receptor (PDB ID: 3NYA) obtained from the Protein Data Bank. Results: A series of piperazino-substituted pyrazolo[3,4-c]-2,7-naphthyridines (3a-j) and 9,11-dimethylpyrimido[1',2':1,5]pyrazolo[3,4-c]-2,7-naphthyridines (4a-j), as well as new heterocyclic systems, i.e., isoxazolo[5,4-c]-2,7-naphthyridines 6a-d, were synthesized and evaluated for their neurotropic activity. The investigation showed that some of these compounds (3a,b,d,f-i and 4a,d,f,i) display high anticonvulsant activity, especially in the test of antagonism with pentylenetetrazol, surpassing the well-known antiepileptic drug ethosuximide. Thus, the most active compounds in the pentylenpotetrazole test are 3h, 3i, and 4i; the ED50 of compound 4i is 23.8, and the therapeutic index is more than 33.6, which is the highest among these three active compounds. On the other hand, they simultaneously exhibit psychotropic (anxiolytic, antidepressant, or sedative) or behavioral depressant) effects. The effective compounds do not cause myorelaxation at the tested doses and have high therapeutic indices. Docking on the most active compounds, i.e., 3h, 3i, and 4i, is in agreement with the experimental results. Conclusions: The studies reveled that some of these compounds (3i, 4a, and 4i) display high anticonvulsant and psychotropic activities. The most active compounds contained methyl and diphenylmethyl groups in the piperazine ring. The docking studies identified compounds 3i, 4i, and 4a as the most potent anticonvulsants, showing strong affinity for GABAA, 5-HT1A receptors, and the SERT transporter. Notably, compound 4i formed two hydrogen bonds with Thr176 and Arg180 on GABAA and exhibited a binding energy (-8.81 kcal/mol) comparable to that of diazepam (-8.90 kcal/mol). It also showed the strongest binding to SERT (-7.28 kcal/mol), stabilized by interactions with Gly439, Ile441, and Arg11. Furthermore, 4i displayed the best docking score with 5-HT1A (-9.10 kcal/mol) due to multiple hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions, supporting its potential as a dual-acting agent targeting both SERT and 5-HT1A.
Keywords: docking studies; isoxazolo[5,4-c]-2,7-naphthyridines; neurotropic activity; pyrazolo[3,4-c]-2,7-naphthyridines; pyrimido[1′,2′:1,5]pyrazolo[3,4-c]-2,7-naphthyridines.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Victor G. Kartsev was employed by InterBioScreen. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- WHO . Epilepsy: A Public Health Imperative. Summary. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2019. (WHO/MSD/MER/19.2). License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
-
- Riney K., Bogacz A., Somerville E., Hirsch E., Nabbout R., Scheffer I.E., Zuberi S.M., Alsaadi T., Jain S., French J., et al. International League Against Epilepsy classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with onset at a variable age: Position statement by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia. 2022;63:1443–1474. doi: 10.1111/epi.17240. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

