Evaluation of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Three Black Cherry Tomato Varieties Grown Under Greenhouse Conditions
- PMID: 40284061
- PMCID: PMC12030121
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14081173
Evaluation of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Three Black Cherry Tomato Varieties Grown Under Greenhouse Conditions
Abstract
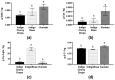
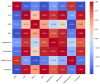
Given the importance of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity in plant defense and human health, this study aimed to evaluate black cherry tomatoes' polyphenol, flavonoid, anthocyanin, and carotenoid content and enzymatic activity under greenhouse conditions. Black cherry tomato varieties-Indigo Cherry Drops, Indigo Rose, and Kumato-were cultivated from seed to the third harvest. Total polyphenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins, β-carotenoids, antioxidant capacity 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), 2,2'-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS), and enzymatic activities, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), proline (PRO), and superoxide dismutase (PAL), were measured and compared. The Kumato variety exhibited significantly higher total polyphenols, flavonoids, and carotenoids, along with enhanced antioxidant activity (DPPH, ABTS) and enzymatic activity (CAT, PAL) compared to Indigo Rose and Indigo Cherry Drops, with free radical inhibition of 87.0% (DPPH) and 74.72% (ABTS). SOD activity was highest in Indigo Rose (0.21 U/mg protein), while proline levels were significantly higher in Kumato and Indigo Cherry Drops (6.40 and 6.63 U/mg protein). These findings highlight the antioxidant potential of black cherry tomatoes and their high potential nutritional value for consumers. Future research should explore how environmental factors influence their biochemical composition and potential applications in functional food.
Keywords: anthocyanins; antioxidants; carotene; enzymatic activity; flavonoids; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Martemucci G., Costagliola C., Mariano M., D’andrea L., Napolitano P., D’Alessandro A.G. Free Radical Properties, Source and Targets, Antioxidant Consumption and Health. Oxygen. 2022;2:48–78. doi: 10.3390/oxygen2020006. - DOI
-
- Akomolafe S., Oboh G. Characterization of Polyphenolic Constituents and Radical Scavenging Ability of Ripe Tomato and Red Pepper Fruits. J. Exp. Integr. Med. 2015;5:61. doi: 10.5455/jeim.080215.or.123. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

