Exploring the Role of TaERF4a in Enhancing Drought Tolerance and Regulating Dehydrin WZY1-2 Gene Expression in Wheat
- PMID: 40284102
- PMCID: PMC12030695
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14081214
Exploring the Role of TaERF4a in Enhancing Drought Tolerance and Regulating Dehydrin WZY1-2 Gene Expression in Wheat
Abstract
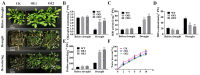
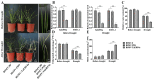
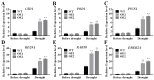
Dehydrins (DHNs) belong to the second family of late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins, which are widely distributed in plants. We cloned a SK3-type DHN gene named WZY1-2 in Zheng yin 1 cultivar of Triticum aestivum. An ERF-type transcription factor TaERF4a was found to be involved in the regulation of the dehydrin WZY1-2 gene in our last report. The stress-responsive ability and dual-luciferase assay demonstrated that TaERF4a positively regulates WZY1-2 gene transcription under stress conditions. In this study, we further characterized the role of the transcription factor TaERF4a in plant drought tolerance. Arabidopsis thaliana heterologously overexpressing TaERF4a exhibited higher survival rate, increased superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, elevated proline and chlorophyll content, and reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) content under drought conditions. Conversely, silencing TaERF4a in Chinese spring wheat using the virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) method increased the sensitivity of plants to drought stress. Furthermore, we identified the specific binding site of TaERF4a in the WZY1-2 promoter. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and dual-luciferase reporter assay demonstrated that TaERF4a activates the expression of the WZY1-2 dehydrin gene through binding to the DRE cis-element in its promoter. Taken together, the results of our study indicate that TaERF4a positively regulates the expression of the dehydrin WZY1-2 gene and enhances drought tolerance in plants.
Keywords: TaERF4a; dehydrin; dual-luciferase assay; transactivation; virus-induced gene silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
An ERF-type transcription factor is involved in the regulation of the dehydrin wzy1-2 gene in wheat.Plant Signal Behav. 2020 Aug 2;15(8):1778920. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2020.1778920. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Plant Signal Behav. 2020. PMID: 32552347 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor TabHLH49 positively regulates dehydrin WZY2 gene expression and enhances drought stress tolerance in wheat.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Jun 5;20(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02474-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32503498 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of K-/S- segments on subcellular localization and dimerization of wheat dehydrin WZY1-2.Plant Signal Behav. 2020 Dec 1;15(12):1827583. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2020.1827583. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Plant Signal Behav. 2020. PMID: 33012219 Free PMC article.
-
The ERF transcription factor TaERF3 promotes tolerance to salt and drought stresses in wheat.Plant Biotechnol J. 2014 May;12(4):468-79. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12153. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Plant Biotechnol J. 2014. PMID: 24393105
-
Wheat and barley dehydrins under cold, drought, and salinity - what can LEA-II proteins tell us about plant stress response?Front Plant Sci. 2014 Jul 9;5:343. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00343. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 25071816 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

