Trans-Kingdom RNA Dialogues: miRNA and milRNA Networks as Biotechnological Tools for Sustainable Crop Defense and Pathogen Control
- PMID: 40284138
- PMCID: PMC12030539
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14081250
Trans-Kingdom RNA Dialogues: miRNA and milRNA Networks as Biotechnological Tools for Sustainable Crop Defense and Pathogen Control
Abstract
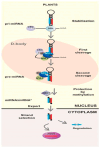
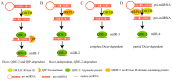
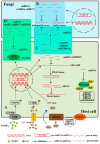
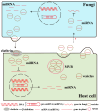
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs approximately 20-24 nucleotides in length, which play a crucial role during gene regulation in plant-pathogen interaction. They negatively regulate the expression of target genes, primarily at the transcriptional or post-transcriptional level, through complementary base pairing with target gene sequences. Recent studies reveal that during pathogen infection, miRNAs produced by plants and miRNA-like RNAs (milRNAs) produced by fungi can regulate the expression of endogenous genes in their respective organisms and undergo trans-kingdom transfer. They can thereby negatively regulate the expression of target genes in recipient cells. These findings provide novel perspectives for deepening our understanding of the regulatory mechanisms underlying plant-pathogen interactions. Here, we summarize and discuss the roles of miRNAs and milRNAs in mediating plant-pathogen interactions via multiple pathways, providing new insights into the functions of these RNAs and their modes of action. Collectively, these insights lay a theoretical foundation for the targeted management of crop diseases.
Keywords: endogenous regulation; fungal milRNA; plant miRNA; plant–pathogen interaction; trans-kingdom regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plant-pathogen interactions: MicroRNA-mediated trans-kingdom gene regulation in fungi and their host plants.Genomics. 2020 Sep;112(5):3021-3035. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.05.021. Epub 2020 May 23. Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32454170
-
MicroRNAs involved in the trans-kingdom gene regulation in the interaction of maize kernels and Fusarium verticillioides.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jul 1;242(Pt 4):125046. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125046. Epub 2023 May 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37245767
-
FoQDE2-dependent milRNA promotes Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense virulence by silencing a glycosyl hydrolase coding gene expression.PLoS Pathog. 2022 May 5;18(5):e1010157. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010157. eCollection 2022 May. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35512028 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Kingdom Regulation of Plant-Derived miRNAs in Modulating Insect Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 28;24(9):7978. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097978. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of microRNAs in abiotic stress response and characteristics regulation of plant.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 26;13:919243. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.919243. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36092392 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

