Quillaja lancifolia Immunoadjuvant Saponins Show Toxicity to Herbivores and Pathogenic Fungi
- PMID: 40284140
- PMCID: PMC12030171
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14081252
Quillaja lancifolia Immunoadjuvant Saponins Show Toxicity to Herbivores and Pathogenic Fungi
Abstract
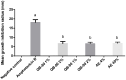
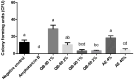
Saponins from leaves of Quillaja lancifolia, a native species from southern Brazil, show potent immunoadjuvant activity in experimental vaccine formulations. The accumulation of the immunoadjuvant saponin fraction QB-90 is induced in cultured leaf disks and seedlings by several stresses and stress signaling molecules, such as osmotic agents, salicylic acid, jasmonic acid, mechanical damage, ultrasound, UV-C radiation, and high light irradiance. These observations suggest a role in plant defense. To further examine this possibility, an investigation of the potential inhibitory role of Q. lancifolia saponins on plant and human pathogenic fungi and two herbivore models was carried out. The screening tests showed that saponin-rich fractions, particularly QB-90, were able to significantly inhibit the growth of Bipolaris micropus, Curvularia inaequalis, Fusarium incarnatum, and Cryptococcus gattii R265. The same metabolites acted as deterrents against the generalist mollusk and insect herbivores Helix aspersa and Spodoptera frugiperda, respectively. Significant reductions in consumption of leaf area and larvae body weight were recorded. Taken together, these data indicate a role for Q. lancifolia saponins in plant defense against diverse herbivores and fungi, having potential as a natural pest control agent and/or as a molecular platform for the development of new environmentally friendly biocide molecules.
Keywords: Quillaja; antifungal; antiherbivore; saponin; specialized metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Accumulation of a bioactive triterpene saponin fraction of Quillaja brasiliensis leaves is associated with abiotic and biotic stresses.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013 May;66:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Feb 16. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23474431
-
Phytotoxicity of Quillaja lancifolia Leaf Saponins and Their Bioherbicide Potential.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 2;12(3):663. doi: 10.3390/plants12030663. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771747 Free PMC article.
-
ISCOM-Matrices Nanoformulation Using the Raw Aqueous Extract of Quillaja lancifolia (Q. brasiliensis).Bionanoscience. 2022;12(4):1166-1171. doi: 10.1007/s12668-022-01023-8. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Bionanoscience. 2022. PMID: 35967762 Free PMC article.
-
Foamy matters: an update on Quillaja saponins and their use as immunoadjuvants.Future Med Chem. 2019 Jun;11(12):1485-1499. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0438. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Future Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31304830 Review.
-
Role of Saponins in Plant Defense Against Specialist Herbivores.Molecules. 2019 May 30;24(11):2067. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112067. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31151268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Leaf Saponins of Quillaja brasiliensis as Powerful Vaccine Adjuvants.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 25;17(8):966. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17080966. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40870989 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Junaid M.D., Gokce A.F., Bostani R. Global agricultural losses and their causes. Bull. Biol. All. Sci. Res. 2024;9:66. doi: 10.54112/bbasr.v2024i1.66. - DOI
-
- Oerke E.C. Crop losses to pests. J. Agr. Sci. 2006;144:31–43. doi: 10.1017/S0021859605005708. - DOI
-
- Mayer A.M. Resistance to herbivores and fungal pathogens: Variations on a common theme? A review comparing the effect of secondary metabolites, induced and constitutive, on herbivores and fungal pathogens. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2004;52:279–292. doi: 10.1560/M3QK-7MMG-813C-MPQ1. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

