Transposon-Associated Small RNAs Involved in Plant Defense in Poplar
- PMID: 40284152
- PMCID: PMC12030527
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14081265
Transposon-Associated Small RNAs Involved in Plant Defense in Poplar
Abstract
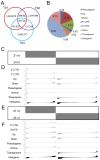
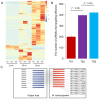
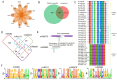
Utilizing high-throughput Illumina sequencing, we examined how small RNA (sRNA) profiles vary in Chinese white poplar (Populus tomentosa) across two pivotal infection stages by the rust fungus Melampsora larici-populina: the biotrophic growth phase (T02; 48 h post infection) and the urediniospore development and dispersal phase (T03; 168 h), both essential for plant colonization and prolonged biotrophic engagement. Far exceeding random expectations, siRNA clusters predominantly arose from transposon regions, with pseudogenes also contributing significantly, and infection-stage-specific variations were notably tied to these transposon-derived siRNAs. As the infection advanced, clusters of 24 nt siRNAs in transposon and intergenic regions exhibited pronounced abundance shifts. An analysis of targets indicated that Populus sRNAs potentially regulate 95% of Melampsora larici-populina genes, with pathogen effector genes showing heightened targeting by sRNAs during the biotrophic and urediniospore phases compared to controls, pointing to selective sRNA-target interactions. In contrast to conserved miRNAs across plant species, Populus-specific miRNAs displayed a markedly greater tendency to target NB-LRR genes. These observations collectively highlight the innovative roles of sRNAs in plant defense, their evolutionary roots, and their dynamic interplay with pathogen coevolution.
Keywords: Melampsora larici-populina; defense response; infection; poplar; small RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

