Mechanism of Green Tea Peptides in Lowering Blood Pressure and Alleviating Renal Injury Induced by Hypertension Through the Ang II/TGF-β1/SMAD Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 40284165
- PMCID: PMC12030635
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17081300
Mechanism of Green Tea Peptides in Lowering Blood Pressure and Alleviating Renal Injury Induced by Hypertension Through the Ang II/TGF-β1/SMAD Signaling Pathway
Abstract
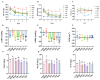
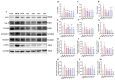
Background/Objectives: The kidney plays a crucial role in regulating normal blood pressure and is one of the major organs affected by hypertension. The present study aimed to investigate the hypotensive and renoprotective effects of four specific green tea peptides extracted from green tea dregs on spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) and to investigate the underlying mechanisms. Methods: Four specific green tea peptides (40 mg/kg) were gavaged to SHRs for 4 weeks, and blood pressure, renal function, renal pathological changes, renal tissue fibrosis indexes, and inflammation indexes were examined in SHRs to analyze the role of the four green tea peptides in alleviating hypertension and its renal injury. Results: The results showed that the four TPs significantly reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure (20-24% and 18-28%) in SHR compared to the model group. Meanwhile, gene levels and protein expression of renal fibrosis-related targets such as phospho-Smad2/3 (p-Smad2/3) (26-47%), Sma- and Mad-related proteins 2/3 (Smad2/3) (19-38%), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) (36-63%), and alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) (58-86%) were also significantly reduced. In addition, the reduced expression levels of medullary differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) (14-36%), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) (58-73%), and nuclear factor-κB p65 (NF-kB p65) (35-78%) in kidneys also confirmed that TPs attenuated renal inflammation in SHR. Therefore, green tea peptides could attenuate the fibrosis and inflammatory responses occurring in hypertensive kidneys by inhibiting the Ang II/TGF-β1/SMAD signaling pathway and MyD88/NF-κB p65/iNOS signaling pathway. Conclusions: The results showed that green tea peptides may be effective candidates for lowering blood pressure and attenuating kidney injury.
Keywords: TGF-β/Smad signaling; hypertension; renal injury; tea polypeptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Icariside II attenuates myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB and the TGF-β1/Smad2 signalling pathway in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Apr;100:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.138. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29421583
-
Benazepril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, alleviates renal injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats by inhibiting advanced glycation end-product-mediated pathways.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009 Mar;36(3):287-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05078.x. Epub 2008 Nov 10. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19018797
-
Benefical therapeutic effect of Chinese Herbal Xinji'erkang formula on hypertension-induced renal injury in the 2-kidney-1-clip hypertensive rats.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014 Aug 23;11(5):16-27. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v11i5.3. eCollection 2014. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25395699 Free PMC article.
-
Central role of dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad in CKD progression and potential targets of its treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:670-681. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.090. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29518614 Review.
-
TGF-β/Smad signaling in kidney disease.Semin Nephrol. 2012 May;32(3):236-43. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.04.002. Semin Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22835454 Review.
References
-
- Kao T.W., Huang C.C. Blood pressure management and renal protection: Revisiting hypertensive nephropathy. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2021;84:911–916. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2020A1515011266, 2022A1515110190, 2023A1515010264, 2024A1515010696/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 202002030202,20212100005,202201011455,2023E04J0781/Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Projects
- 2021ZDZX002/Qingyuan Science and Technology Plan Projects
- 202126TD/Agricultural competitive industry discipline team building project of Guangdong Academy of Ag-ricultural Sciences
- R2021YJ-YB3014,R2024YJ-YB3005/Special fund project for introduction of scientific and technological talents of Guangdong Acade-my of Agricultural Sciences
- 202115, 202135/Innovation Fund projects of Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences
- R2022PY-QY010/Special fund for scientific innovation strategy-construction of high level Academy of Agriculture Science
- 2021CX02/the Innovation Fund projects of Guangdong Key Laboratory of Tea Plant Resources Innovation and Utilization
- KTP20210090/The project of guang dong province rural science and technology commissioner stationed in the village and town
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

