Effects of GLP-1 Analogues and Agonists on the Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40284168
- PMCID: PMC12029897
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17081303
Effects of GLP-1 Analogues and Agonists on the Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: GLP-1 analogues are a relatively new class of medications that form the cornerstone of diabetes treatment. They possess invaluable glucose-lowering properties without hypoglycemic effects as well as strong cardioprotective effects. The gut microbiome has become the focus of numerous studies, demonstrating its influence not only on the gut but also on the overall well-being of the entire body. However, the effects of GLP-1 analogs on gut microbiota remain uncertain.
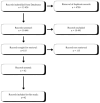
Scope of review: Our systematic review (based on PRISMA guidelines) aimed to gather knowledge on the effects of GLP-1 analogue medications on the composition, richness, and abundance of gut microbiota in both animal and human models.
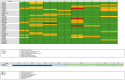
Conclusions: Thirty-eight studies were included in this systematic review. GLP-1 analogues have demonstrated a notable impact on the composition, richness, and diversity of gut microbiota. We can conclude, following the obtained research results of our study, that liraglutide promotes the growth of beneficial genera relevant for beneficial metabolic functions. Exenatide and exendin-4 administration showed various effects on the microbiome composition in animal and human studies. In animal models, it increased genera associated with improved metabolism; however, in human models, genera linked to better metabolic functions and escalated inflammation increased. Following dulaglutide administration, increases in Bacteroides, Akkermansia, and Ruminococcus, genera connected to an improved metabolic model, were significant. Finally, varied results were obtained after semaglutide treatment, in which A. muciniphila, known for its positive metabolic functions, increased; however, microbial diversity decreased. Semaglutide treatment provided various results indicating many confounding factors in semaglutide's impact on the gut microbiota. Results varied due to dissimilarities in the studied populations and the duration of the studies. Further research is essential to confirm these findings and to better recognize their implications for the clinical outcomes of patients.
Keywords: GLP-1 agonists; GLP-1 analogues; microbiome; microbiota; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Agonists for Psychiatric Symptoms: A Systematic Review.Brain Behav. 2025 Jul;15(7):e70661. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70661. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40635383 Free PMC article.
-
Newer agents for blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Jul;14(36):1-248. doi: 10.3310/hta14360. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20646668
-
Mazdutide, a dual agonist targeting GLP-1R and GCGR, mitigates diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction: mechanistic insights from multi-omics analysis.EBioMedicine. 2025 Jul;117:105791. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105791. Epub 2025 Jun 6. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40479843 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the injectable weight-loss medications, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, on reproductive health in non-polycystic ovary syndrome state.Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2025 Aug 1;37(4):175-181. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0000000000001044. Epub 2025 May 12. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2025. PMID: 40459435 Review.
Cited by
-
Probiotics as Antioxidant Strategy for Managing Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 22;14(7):767. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070767. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dionysus or apollo, skeletal muscle mass changes in type 2 diabetes with sarcopenia receiving GLP-1 receptor agonist: systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Aug 6;17(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01877-4. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40770817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapeutics for Metabolic Disorders: Mechanistic Insights into the Synergy of Probiotic-Fermented Herbal Bioactives.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 7;26(12):5486. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125486. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bidirectional Interactions Between the Gut Microbiota and Incretin-Based Therapies.Life (Basel). 2025 May 23;15(6):843. doi: 10.3390/life15060843. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40566497 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li S., Vandvik P.O., Lytvyn L., Guyatt G.H., Palmer S.C., Rodriguez-Gutierrez R., Foroutan F., Agoritsas T., Siemieniuk R.A.C., Walsh M., et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors or GLP-1 receptor agonists for adults with type 2 diabetes: A clinical practice guideline. BMJ. 2021;373:n1091. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n1091. Erratum in BMJ 2022, 377, o1080. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.o1080 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- International Hypoglycaemia Study Group Hypoglycaemia, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in diabetes: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7:385–396. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30315-2. Erratum in Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30139-1 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- SAXENDA® (Liraglutide) Injection 3 mg Medication Guide. [(accessed on 5 April 2025)]. Available online: https://www.novo-pi.com/saxenda.pdf#guide.
-
- Wegovy® (Semaglutide) Injection 2.4 mg Medication Guide. [(accessed on 5 April 2025)]. Available online: https://www.novo-pi.com/wegovy.pdf#guide.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials