Lion's Mane Mushroom (Hericium erinaceus): A Neuroprotective Fungus with Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antimicrobial Potential-A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40284172
- PMCID: PMC12030463
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17081307
Lion's Mane Mushroom (Hericium erinaceus): A Neuroprotective Fungus with Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antimicrobial Potential-A Narrative Review
Abstract
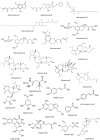
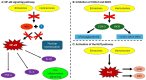
Hericium erinaceus, commonly known as lion's mane mushroom, has gained increasing scientific interest due to its rich composition of bioactive compounds and diverse health-promoting properties. This narrative review provides a comprehensive overview of the nutritional and therapeutic potential of H. erinaceus, with a particular focus on its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities. A structured literature search was performed using databases such as PubMed, Scopus, Science Direct, Web of Science, Science Direct, and Google Scholar. Studies published in the last two decades focusing on H. erinaceus' bioactive compounds were included. The chemical composition of H. erinaceus includes polysaccharides, terpenoids (hericenones and erinacines), and phenolic compounds, which exhibit potent antioxidant effects by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inducing endogenous antioxidant enzymes. Additionally, H. erinaceus shows promising antimicrobial activity against bacterial and fungal pathogens, with potential applications in combating antibiotic-resistant infections. The mushroom's capacity to stimulate nerve growth factor (NGF) synthesis has highlighted its potential in preventing and managing neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Advances in biotechnological methods, including optimized cultivation techniques and novel extraction methods, may further enhance the bioavailability and pharmacological effects of H. erinaceus. Despite promising findings, clinical validation remains limited. Future research should prioritize large-scale clinical trials, the standardization of extraction methods, and the elucidation of pharmacokinetics to facilitate its integration into evidence-based medicine. The potential of H. erinaceus as a functional food, nutraceutical, and adjunct therapeutic agent highlights the need for interdisciplinary collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and regulatory bodies.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; monkey head mushroom; natural antimicrobials; polysaccharides; pom-pom mushroom; terpenoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chemistry, Nutrition, and Health-Promoting Properties of Hericium erinaceus (Lion's Mane) Mushroom Fruiting Bodies and Mycelia and Their Bioactive Compounds.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Aug 19;63(32):7108-23. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02914. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 26244378 Review.
-
Neurotrophic and Neuroprotective Effects of Hericium erinaceus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 3;24(21):15960. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115960. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute effects of a standardised extract of Hericium erinaceus (Lion's Mane mushroom) on cognition and mood in healthy younger adults: a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled study.Front Nutr. 2025 Apr 10;12:1405796. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1405796. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40276537 Free PMC article.
-
Structures, biological activities, and industrial applications of the polysaccharides from Hericium erinaceus (Lion's Mane) mushroom: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Apr;97:228-237. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.040. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28087447 Review.
-
Identification and Reconstitution of the First Two Enzymatic Steps for the Biosynthesis of Bioactive Meroterpenoids from Hericium erinaceus (Lion's Mane Mushroom).Molecules. 2024 Nov 26;29(23):5576. doi: 10.3390/molecules29235576. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39683734 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Supporting Neurologic Health with Mushroom Nutrition.Nutrients. 2025 May 2;17(9):1568. doi: 10.3390/nu17091568. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40362877 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Contato A.G., Aranha G.M., de Abreu Filho B.A., Peralta R.M., de Souza C.G.M. Evaluation of the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of the culinary-medicinal mushroom Lentinula boryana (Agaricomycetes) from Brazil. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms. 2021;23:1–7. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2021039966. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 313119/2020-1/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- E-26/200.891/2021/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- E-26/203.745/2024/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- 001/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

