Wine Consumption and Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40284187
- PMCID: PMC12030585
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17081322
Wine Consumption and Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
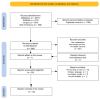
Background/Objectives: Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality, with tobacco smoking being the primary risk factor. However, a significant percentage of lung cancer patients are non-smokers, suggesting the involvement of other risk factors, including alcohol consumption. The IARC classifies ethanol as a Group 1 carcinogen, but unlike other alcoholic beverages, wine contains polyphenols with potential health benefits. Some meta-analyses even suggest a protective effect, which led us to conduct our own meta-analysis to further investigate this possible correlation. Methods: We conducted a systematic review and stratified the risk across population subgroups based on smoking status and gender. We then performed a categorical "highest vs. lowest" meta-analysis, comparing heavy consumers with very occasional drinkers, using a random-effects model. Only studies examining the risk of developing lung cancer in wine drinkers were included, excluding those with different outcomes, non-primary, ineligible populations, or involving pregnant women. The literature search was conducted in three databases: PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science. The risk of bias was assessed with the Newcastle-Ottawa quality rating scale for both case-control and cohort studies (NOS), while statistical analyses were performed using the ProMeta 3.0 software. Results: The overall analysis showed a non-statistically significant 11% reduction in lung cancer risk (OR = 0.89; 95% CI: 0.77-1.03). The analysis among smokers revealed a significant 22% reduction in lung cancer risk associated with wine consumption (OR = 0.78; 95% CI: 0.62-0.97). However, this effect was lost when the analysis was conducted separately based on the study design. Conclusions: No correlation emerged between wine consumption and lung cancer incidence, either in a protective sense or in terms of increased risk. However, further studies are needed to investigate this correlation more accurately, particularly among non-smokers.
Keywords: lung cancer; meta-analysis; wine consumption; wine intake.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

