Breastfeeding: The Multifaceted Impact on Child Development and Maternal Well-Being
- PMID: 40284191
- PMCID: PMC12030032
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17081326
Breastfeeding: The Multifaceted Impact on Child Development and Maternal Well-Being
Abstract
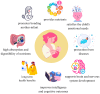
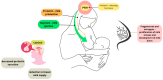
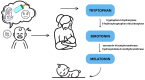
Breastfeeding is recognized as the gold standard in infant nutrition, providing necessary nutrients for optimal growth and development. Beyond its nutritional function, breastfeeding has numerous benefits for both mother and child. This literature review examines the effects of breastfeeding on the development of the nervous and immune systems, its influence on cognitive development, and the impact of stress on lactation. In addition, it explores the emotional effects of breastfeeding on mothers, the challenges associated with exclusive breastfeeding, and the process of weaning along with its implications for both mother and infant. It is indicated that stress significantly affects lactation regulation, with elevated cortisol levels potentially disrupting hormonal balance. Furthermore, the essential roles of oxytocin, sialic acid, and docosahexaenoic acid in infant brain development and cognitive functions are highlighted. Breastfeeding is associated with the regulation of the baby's sleep through the effects of tryptophan, serotonin, and melatonin, which at the same time provide the baby with a sense of security with the mother. It is indicated that women who breastfeed are less likely to suffer from mental health problems and are at a lower risk of hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. The weaning process is often a difficult time for mother and child; thus, it should be introduced gradually to minimize stress, anxiety, and potential mood disturbances in the mother.
Keywords: breastfeeding; infancy; lactation; psychology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Risch L., Hotzy F., Vetter S., Hiller S., Wallimann K., Seifritz E., Mötteli S. Assessment of Nutritional Status and Risk of Malnutrition Using Adapted Standard Tools in Patients with Mental Illness and in Need of Intensive Psychiatric Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2023;20:109. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Romero-Velarde E., Delgado-Franco D., García-Gutiérrez M., Gurrola-Díaz C., Larrosa-Haro A., Montijo-Barrios E., Muskiet F.A.J., Vargas-Guerrero B., Geurts J. The Importance of Lactose in the Human Diet: Outcomes of a Mexican Consensus Meeting. Nutrients. 2019;11:2737. doi: 10.3390/nu11112737. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical