Biological Effect of Mycosporine-Gly-Ser (Shinorine) Against Bis-Retinoid N-Retinyl- N-Retinylidene Ethanolamine- and Blue-Light-Induced Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cell Damage
- PMID: 40284227
- PMCID: PMC12030148
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17081363
Biological Effect of Mycosporine-Gly-Ser (Shinorine) Against Bis-Retinoid N-Retinyl- N-Retinylidene Ethanolamine- and Blue-Light-Induced Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cell Damage
Abstract
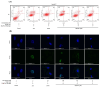
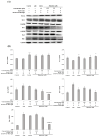
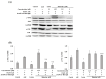
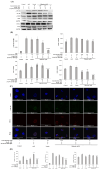
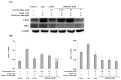
Shinorine is a mycosporine-like amino acid isolated from laver (Porphyra dentata), and interest in its functionality has increased recently due to increased production using yeast. There have been few reports on the pharmacological activity of shinorine, and we sought to find the pharmacological significance of shinorine. In the present study, we investigated the pharmacological effects of shinorine purified from Porphyra dentata on ARPE-19 cells. First, when ARPE-19 cells were treated with bis-retinoid N-retinyl-N-retinylidene ethanolamine (A2E) and blue light (BL), cytotoxicity increased, and apoptosis was observed. We investigated the effects of shinorine on A2E- and BL-induced cytotoxicity and changes in apoptotic factors, inflammation, and carbonyl stress. A2E and BL exposure increased ARPE-19 cell apoptosis, but this increase was attenuated by shinorine in a concentration-dependent manner. Treatment with A2E and BL induced ARPE-19 cell apoptosis, but treatment with shinorine decreased the apoptotic factors, such as MAPKs. Shinorine reduced p-JNK and p-P38, which were increased by A2E and BL. In addition, shinorine was found to regulate inflammatory proteins and proteins associated with carbonyl stress. In conclusion, shinorine may suppress cell damage caused by A2E treatment and BL exposure at the cellular level by regulating various cell death and inflammatory response pathways.
Keywords: ARPE-19; Porphyra dentata; black paper; eye health; mycosporine-like amino acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
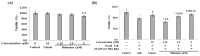
Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of 7S,15R-Dihydroxy-16S,17S-Epoxy-Docosapentaenoic Acid (diHEP-DPA) against Blue Light-Induced Retinal Damages in A2E-Laden ARPE-19 Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 13;13(8):982. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080982. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199228 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers GRP78 and CHOP induced by oxidative stress in blue light-mediated damage of A2E-containing retinal pigment epithelium cells.Ophthalmic Res. 2014;52(4):224-33. doi: 10.1159/000363387. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Ophthalmic Res. 2014. PMID: 25402962
-
Toxic effects of A2E in human ARPE-19 cells were prevented by resveratrol: a potential nutritional bioactive for age-related macular degeneration treatment.Arch Toxicol. 2020 Feb;94(2):553-572. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02637-w. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Arch Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31792590
-
Quercetin-3-O-α-l-arabinopyranoside protects against retinal cell death via blue light-induced damage in human RPE cells and Balb-c mice.Food Funct. 2018 Apr 25;9(4):2171-2183. doi: 10.1039/c7fo01958k. Food Funct. 2018. PMID: 29541735
-
A2E and Lipofuscin.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;134:449-63. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26310170 Review.
References
-
- Ficek D., Dera J., Woźniak B. UV absorption reveals mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in Tatra mountain lake phytoplankton. Oceanologia. 2013;55:599–609. doi: 10.5697/oc.55-3.599. - DOI
-
- Babele P.K., Singh G., Singh A., Kumar A., Tyagi M.B., Sinha R.P. UV-B radiation and temperature stress-induced alterations in metabolic events and defense mechanisms in a bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017;39:248. doi: 10.1007/s11738-017-2540-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

