Development and Characterization of Polymeric Films Loaded with Terbinafine for Fungal Infection Treatment
- PMID: 40284269
- PMCID: PMC12030444
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17081004
Development and Characterization of Polymeric Films Loaded with Terbinafine for Fungal Infection Treatment
Abstract
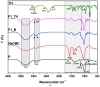
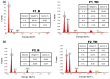
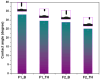
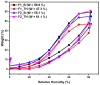
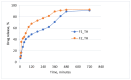
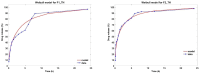
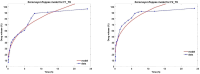
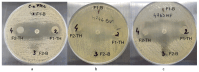
Topical approaches to dermatophytosis have the advantage of targeted therapy and minimal side effects and are patient-friendly. The present study focused on obtaining thin, flexible, and transparent bioadhesive polymeric films loaded with terbinafine hydrochloride (TH), in order to be administered to the skin affected by fungal infection. Polymeric films based on pullulan (P), oxidized pullulan (T-OP), sodium carboxymethylcellulose (NaCMC), and glycerin were obtained by the casting and evaporation technique, and the solubility of the drug was significantly increased by micellar solubilization with Tween-80, thus avoiding the use of organic solvents. Physico-chemical characterization through the FTIR technique and EDX analysis indicates the absence of strong interactions between the drug and the polymer, and the loading efficiency highlights the uniform distribution of the drug. The mechanical properties, bioadhesion, contact angle, and water sorption capacity highlight optimal adhesion parameters on the skin. In vitro studies indicate a prolonged drug release, in the first 300 min, of 80% and 60% for F2_TH and F1_TH, respectively, and the release kinetics follow the Weibull model. Significant antifungal activity was obtained for both polymeric films. The biocompatibility of the ingredients, the gentle technique for obtaining the films, and the results obtained from their analysis represent promise for their applicability in topical antifungal treatment.
Keywords: antifungal activity; bioadhesion; dermatophytosis; fungal infection; micellar solubilization; terbinafine hydrochloride; the release kinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
New Polyurethane Nail Lacquers for the Delivery of Terbinafine: Formulation and Antifungal Activity Evaluation.J Pharm Sci. 2017 Jun;106(6):1570-1577. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.02.017. Epub 2017 Mar 3. J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28263845
-
Polymeric Nanocapsules Containing Ozonated Oil and Terbinafine Hydrochloride as a Potential Treatment Against Dermatophytes.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023 Oct 2;24(7):198. doi: 10.1208/s12249-023-02657-x. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023. PMID: 37783861
-
Terbinafine hydrochloride loaded liposome film formulation for treatment of onychomycosis: in vitro and in vivo evaluation.J Liposome Res. 2016;26(2):163-73. doi: 10.3109/08982104.2015.1067892. Epub 2015 Jul 30. J Liposome Res. 2016. PMID: 26226352
-
PLGA based film forming systems for superficial fungal infections treatment.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021 Aug 1;163:105855. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2021.105855. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 33872699
-
Development and Characterization of Terbinafine-Loaded Nanoemulgel for Effective Management of Dermatophytosis.Gels. 2023 Nov 12;9(11):894. doi: 10.3390/gels9110894. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37998984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shoaiba S., Kaurb G., Yusufc K., Yusuf N. Herbal medicines and skin disorders. In: Sarwat M., Siddique H., editors. Herbal Medicines. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2022. pp. 307–328.
-
- Havlickova B., Czaika V.A., Friedrich M. Epidemiological trends in skin mycoses worldwide. Mycoses. 2008;51:2–15. - PubMed
-
- Gaba B., Fazil M., Khan S., Ali A., Baboota S., Ali J. Nanostructured lipid carrier system for topical delivery of terbinafine hydrochloride. Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ. 2015;53:147–159. doi: 10.1016/j.bfopcu.2015.10.001. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

