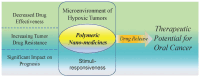
Development of Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Nanomedicines in Hypoxic Tumors and Their Therapeutic Promise in Oral Cancer
- PMID: 40284275
- PMCID: PMC12030766
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17081010
Development of Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Nanomedicines in Hypoxic Tumors and Their Therapeutic Promise in Oral Cancer
Abstract
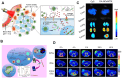
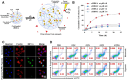
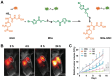
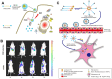
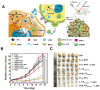
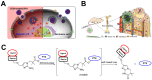
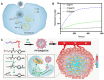
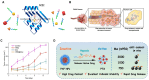
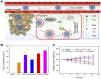
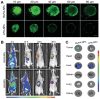
Hypoxic tumors pose considerable obstacles to cancer treatment, as diminished oxygen levels can impair drug effectiveness and heighten therapeutic resistance. Oral cancer, a prevalent malignancy, encounters specific challenges owing to its intricate anatomical structure and the technical difficulties in achieving complete resection, thereby often restricting treatment efficacy. The impact of hypoxia is particularly critical in influencing both the treatment response and prognosis of oral cancers. This article summarizes and examines the potential of polymer nanomedicines to address these challenges. By engineering nanomedicines that specifically react to the hypoxic tumor microenvironment, these pharmaceuticals can markedly enhance targeting precision and therapeutic effectiveness. Polymer nanomedicines enhance therapeutic efficacy while reducing side effects by hypoxia-targeted accumulation. The article emphasizes that these nanomedicines can overcome the drug resistance frequently observed in hypoxic tumors by improving the delivery and bioavailability of anticancer agents. Furthermore, this review elucidates the design and application of polymer nanomedicines for treating hypoxic tumors, highlighting their transformative potential in cancer therapy. Finally, this article gives an outlook on stimuli-responsive polymeric nanomedicines in the treatment of oral cancer.
Keywords: hypoxic tumors; oral cancer; polymeric nanomedicines; stimulus response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biomaterial-Based Responsive Nanomedicines for Targeting Solid Tumor Microenvironments.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 26;16(2):179. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020179. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of stimuli responsive polymeric nanomedicines modulating tumor microenvironment for improved cancer therapy.Med Rev (2021). 2023 Mar 17;3(1):4-30. doi: 10.1515/mr-2022-0048. eCollection 2023 Feb. Med Rev (2021). 2023. PMID: 37724108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in dual- and multi-responsive nanomedicines for precision cancer therapy.Biomaterials. 2022 Dec;291:121906. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121906. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Biomaterials. 2022. PMID: 36395660 Review.
-
Tumor-Targeted Nanomedicine for Immunotherapy.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Dec 15;53(12):2765-2776. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00518. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 33161717 Review.
-
Tumor Abnormality-Oriented Nanomedicine Design.Chem Rev. 2023 Sep 27;123(18):10920-10989. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00062. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Chem Rev. 2023. PMID: 37713432 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- No:124ZXGZSY00100/Tianjin Key Projects of Public Health Science and Technology Major Projects
- TJWJ2023XK026/Tianjin Health Science and Technology Project, Key Medical Discipline Special Project
- No:2024ZXZD011/Scientific Research Project of Tianjin Education Commission (Natural Science)
- No:2023179/Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Project of Tianjin Municipal Health and Health Committee
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

