Barriers and Strategies for Oral Peptide and Protein Therapeutics Delivery: Update on Clinical Advances
- PMID: 40284395
- PMCID: PMC12030352
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040397
Barriers and Strategies for Oral Peptide and Protein Therapeutics Delivery: Update on Clinical Advances
Abstract
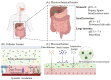
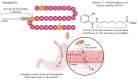
Peptide and protein (PP) therapeutics are highly specific and potent biomolecules that treat chronic and complex diseases. However, their oral delivery is significantly hindered by enzymatic degradation, instability, and poor permeability through the gastrointestinal (GI) epithelium, resulting in low bioavailability. Various strategies have emerged as transformative solutions to address existing challenges, offering enhanced protection, stabilization, and absorption of PPs. These strategies primarily focus on two major challenges: protecting the PP against harsh conditions and enhancing permeation across the intestinal membrane. Innovative approaches such as pH modulation and incorporation of enzyme inhibitors are usually used to mitigate proteolytic degradation of PP during transit across the GI tract. In a similar vein, absorption enhancers and prodrug strategies facilitate epithelial transport, while targeted delivery systems focus on specific areas of the GI tract to enhance absorption. Likewise, mucus-penetrating and mucoadhesive strategies have enhanced retention and interaction with epithelial cells, effectively overcoming barriers like the mucus layer and tight epithelial junctions. Furthermore, structural modifications such as lipidation, peptide cyclization, and polyethylene glycosylation are promising alternatives to render stability, prolong circulation time, and membrane permeability. In particular, functional biomaterials, active targeting, and lymphatic transport strategies have provided new platforms for oral PP delivery. Advancing in materials science, nanotechnology, and the disruption of medical devices holds new frontiers to overcome barriers. Despite substantial advancements, the limited success in clinical translation underscores the urgency of innovative strategies. This review presents oral PPs as a promising platform, highlighting the key barriers and strategies to transform their therapeutic landscapes.
Keywords: bioavailability enhancement; enzymatic degradation; oral drug delivery; protein therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
K.Y.C. is the founder of NVience Inc. The other author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Oral delivery of protein and peptide therapeutics.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2025;212:355-387. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2024.11.003. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40122651 Review.
-
An Update on Pharmaceutical Strategies for Oral Delivery of Therapeutic Peptides and Proteins in Adults and Pediatrics.Children (Basel). 2020 Dec 19;7(12):307. doi: 10.3390/children7120307. Children (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33352795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Current and Promising Oral Delivery Methods for Protein- and Peptide-Based Drugs.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 9;25(2):815. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020815. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral peptide delivery: Translational challenges due to physiological effects.J Control Release. 2018 Oct 10;287:167-176. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.08.032. Epub 2018 Aug 23. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 30145135 Review.
-
Nanomedicine for Oral Delivery: Strategies to Overcome the Biological Barriers.Small Methods. 2025 Jun 16:e2500624. doi: 10.1002/smtd.202500624. Online ahead of print. Small Methods. 2025. PMID: 40522197 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in the therapeutics and modes of action of a range of agents used to treat ulcerative colitis and related inflammatory conditions.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Aug 15. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01906-8. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40815427 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

