Anti-Breast Cancer Properties and In Vivo Safety Profile of a Bis-Carbazole Derivative
- PMID: 40284411
- PMCID: PMC12030284
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040415
Anti-Breast Cancer Properties and In Vivo Safety Profile of a Bis-Carbazole Derivative
Abstract
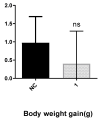
Background: Carbazoles represent one of the most important classes of nitrogen-based tricyclic aromatic heterocycles and are present in natural sources and chemically obtained drugs. Recently, several research groups disclosed their large biological and chemical applications in different fields, leading to an increased interest towards this class of molecules. Some of the obtained derivatives have been successfully employed in the clinical treatment of different tumor types, but the onset of heavy side effects impaired their efficacy and discouraged their use. Pursuing the aim of obtaining carbazoles with less negative features, a lot of chemically modified compounds have been produced and evaluated. Objectives/Methods: In this paper, we describe the in vitro and in vivo evaluation of a bis-carbazole derivative with strong anticancer properties against two breast cancer cell lines. Results: This compound has been found to impact the cell cytoskeleton dynamics, triggering the activation of some key proteins playing a role in the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Equally important, this derivative has been found to be selective for cancer cells and has shown a safe profile in Balb/c-treated mice. Conclusions: Overall, the disclosed outcomes represent an important landmark for encouraging further studies directed toward the potentiation of this lead to be potentially exploited in both preclinical and clinical applications.
Keywords: anticancer; apoptosis; carbazole derivatives; cytoskeleton; toxicity studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures













References
-
- Tiwari A., Mishra B. Diverse pharmacological actions of potential carbazole derivatives by influencing various pathways of molecular signaling. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2024;10:77. doi: 10.1186/s43094-024-00650-0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

