Utilizing Nanoparticles of Hesperidin Loaded on Layered Double Hydroxide to Reduce Hepatotoxicity Caused by Paracetamol in Rats: Controlling of Biotransformation, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis
- PMID: 40284423
- PMCID: PMC12030007
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040429
Utilizing Nanoparticles of Hesperidin Loaded on Layered Double Hydroxide to Reduce Hepatotoxicity Caused by Paracetamol in Rats: Controlling of Biotransformation, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis
Abstract
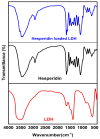
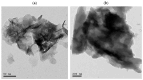
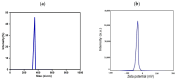
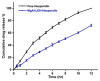
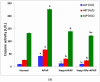
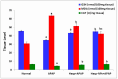
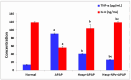
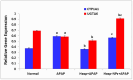
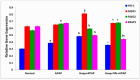
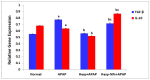
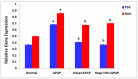
Background/Objectives: The most used antipyretic and pain relief treatment is paracetamol (acetaminophen), also known as N-acetyl-para-aminophenol (APAP). However, it is considered potentially hazardous if consumed repeatedly in large doses or over prolonged periods. This investigation explores the effectiveness of hesperidin (Hesp) and Hesp loaded on layered double hydroxide nanoparticles (Hesp-NPs) in inhibiting the progression of acute hepatotoxicity in rats induced by APAP. Methods: LDH-Hesp-NPs were prepared and characterized. Male Wistar rats were orally treated with Hesp and Hesp-NPs at the same adjusted dose (100 mg/kg) every other day for six weeks. After 2 h of the first doses of Hesp and Hesp-NPs, the rats received one oral dose of APAP (750 mg/kg). Results: Administering of Hesp and Hesp-NPs to APAP-treated rats significantly reduced oxidant parameter (malondialdehyde) and serum enzymes (ALT, AST, LDH, and ALP) associated with liver function. Antioxidant markers in the liver, such as catalase and glutathione, also increased notably. Moreover, Hesp and Hesp-NPs enhanced the mRNA expression of liver UGT1A6, IL-10, and HO-1. Conversely, the mRNA expressions of liver CYP1A1, KEAP1, TGF-β, P53, and BAX decreased. These improvements in biochemical and molecular markers were corroborated by liver histopathology. Conclusions: Hesp and Hesp-NPs protect significantly against APAP-induced hepatotoxicity in male Wistar rats. Hesp-NPs treatment was more potent. The protective effects may be mediated via modulation of APAP biotransformation, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis.
Keywords: hepatotoxicity; hesperidin nanoparticles; layered double hydroxide; paracetamol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

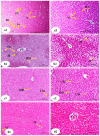
References
-
- Halim A., Nur N.M., El-Agamy E.-S., Ibrahim A. Protective effect of hesperidin (HDN) on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatic toxicity in male albino rats. AIJCR. 2017;8:20328–20338.
-
- Dart R.C., Bailey E. Does therapeutic use of acetaminophen cause acute liver failure? Pharmacotherapy. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2007;27:1219–1230. - PubMed
-
- Dar A., Saxena R., Bansal S. Hepatoprotection: A Hallmark of Citrullus colocynthis L. against Paracetamol Induced Hepatotoxicity in Swiss Albino Rats. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2012;3:1022–1027.
-
- Ahmed O.M. Natural Flavonoids: Chemistry, Therapeutic Potentials, Therapeutic Targets and Mechanisms of Actions. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021;27:455. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

