Modified-Release Pulmonary Delivery Systems for Labile Bioactives: Design, Development, and Applications
- PMID: 40284465
- PMCID: PMC12030271
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040470
Modified-Release Pulmonary Delivery Systems for Labile Bioactives: Design, Development, and Applications
Abstract
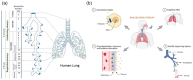
Pulmonary delivery of bioactives has shown to be a promising route for the treatment of respiratory conditions, however, numerous physiological barriers, such as mucociliary clearance and immune responses, pose significant hurdles to treatment efficacy. These barriers specifically affect labile bioactives such as mRNA, peptides, proteins, and probiotics, which are susceptible to degradation due to the prevailing conditions. Various drug delivery platforms have been developed to address these challenges, including, among others, polymeric nanoparticles, micelles, liposomes, and solid lipid nanoparticles that encapsulate and protect the labile bioactives during formulation and administration, enabling improved bioavailability, sustained release, and enhanced formulation stability, while further modification of these platforms allows for targeted drug delivery. This review explores the advanced drug delivery systems that have been designed to protect and release labile active agents in a controlled and targeted manner to the lung, with a specific focus provided on the physiological barriers to effective pulmonary delivery and the formulation considerations to overcome these challenges. The outlook of this pertinent field of study has additionally been provided, highlighting the significant potential of the pulmonary delivery of labile bioactive agents for the prevention and treatment of a variety of respiratory ailments.
Keywords: mRNA delivery; nanosystems; physiological barriers; probiotics; proteins and peptides; respiratory system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Morales J.O., Fathe K.R., Brunaugh A., Ferrati S., Li S., Montenegro-Nicolini M., Mousavikhamene Z., McConville J.T., Prausnitz M.R., Smyth H.D. Challenges and future prospects for the delivery of biologics: Oral mucosal, pulmonary, and transdermal routes. AAPS J. 2017;19:652–668. - PubMed
-
- Byron P.R. Physicochemical effects on lung disposition of pharmaceutical aerosols. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1993;18:223–229.
-
- Moutinho C.G., Matos C.M., Teixeira J.A., Balcão V.M. Nanocarrier possibilities for functional targeting of bioactive peptides and proteins: State-of-the-art. J. Drug Target. 2012;20:114–141. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

