Targeting Regulatory Noncoding RNAs in Human Cancer: The State of the Art in Clinical Trials
- PMID: 40284466
- PMCID: PMC12030637
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040471
Targeting Regulatory Noncoding RNAs in Human Cancer: The State of the Art in Clinical Trials
Abstract
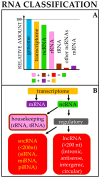
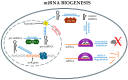
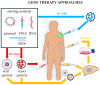
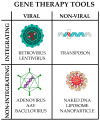
Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) are a heterogeneous group of RNA molecules whose classification is mainly based on arbitrary criteria such as the molecule length, secondary structures, and cellular functions. A large fraction of these ncRNAs play a regulatory role regarding messenger RNAs (mRNAs) or other ncRNAs, creating an intracellular network of cross-interactions that allow the fine and complex regulation of gene expression. Altering the balance between these interactions may be sufficient to cause a transition from health to disease and vice versa. This leads to the possibility of intervening in these mechanisms to re-establish health in patients. The regulatory role of ncRNAs is associated with all cancer hallmarks, such as proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, metastasis, and genomic instability. Based on the function performed in carcinogenesis, ncRNAs may behave either as oncogenes or tumor suppressors. However, this distinction is not rigid; some ncRNAs can fall into both classes depending on the tissue considered or the target molecule. Furthermore, some of them are also involved in regulating the response to traditional cancer-therapeutic approaches. In general, the regulation of molecular mechanisms by ncRNAs is very complex and still largely unclear, but it has enormous potential both for the development of new therapies, especially in cases where traditional methods fail, and for their use as novel and more efficient biomarkers. Overall, this review will provide a brief overview of ncRNAs in human cancer biology, with a specific focus on describing the most recent ongoing clinical trials (CT) in which ncRNAs have been tested for their potential as therapeutic agents or evaluated as biomarkers.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer; clinical trial; noncoding RNA; oncological therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noncoding RNAs in DNA Damage Response: Opportunities for Cancer Therapeutics.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1699:3-21. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7435-1_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29086365
-
The role of noncoding RNAs in epithelial cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2020 Mar 12;6:13. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-0247-6. eCollection 2020. Cell Death Discov. 2020. PMID: 32194993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the functional landscape and therapeutic implications of noncoding RNAs in the TGF-β signaling pathway in colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Mar;255:155158. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155158. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38320438 Review.
-
Role of noncoding RNAs and untranslated regions in cancer: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Aug 19;101(33):e30045. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030045. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35984196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double-edged effects of noncoding RNAs in responses to environmental genotoxic insults: Perspectives with regards to molecule-ecology network.Environ Pollut. 2019 Apr;247:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.014. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Environ Pollut. 2019. PMID: 30654255 Review.
References
-
- What Is Cancer. [(accessed on 22 December 2024)]; Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/what-is-cancer.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

