Hydrogel Containing Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Origanum vulgare Essential Oil for Burn Wounds: Antimicrobial Efficacy Using Ex Vivo and In Vivo Methods Against Multidrug-Resistant Microorganisms
- PMID: 40284498
- PMCID: PMC12030619
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040503
Hydrogel Containing Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Origanum vulgare Essential Oil for Burn Wounds: Antimicrobial Efficacy Using Ex Vivo and In Vivo Methods Against Multidrug-Resistant Microorganisms
Abstract
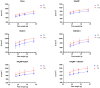
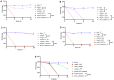
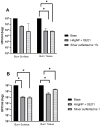
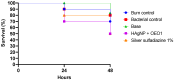
Background/Objectives: Wounds from burns are susceptible to infections, allowing multidrug-resistant microorganisms to complicate treatments and patient recovery. This highlights the development of new strategies to control these microorganisms. This work evaluated the antibacterial activity of hydrogels containing biogenic silver nanoparticles (bio-AgNP) and Origanum vulgare essential oil (OEO) against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Methods: The formulations were subjected to organoleptic, pharmacotechnical, and stability characterization and antimicrobial activity assessment by time-kill tests and alternative methods, an ex vivo model using porcine skin, and an in vivo model using Galleria mellonella. Results: All hydrogels maintained their stability after the thermal stress. The hydrogel containing bio-AgNP + OEO 1% (HAgNP + OEO1) presented bactericidal effectiveness, within 2 h, against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative multidrug-resistant bacteria in the time-kill test. For alternative testing, HAgNP + OEO1 was compared with 1% silver sulfadiazine (SS) and the base formulation. In the ex vivo test, both HAgNP + OEO1 and SS treatments showed a similar reduction in superficial washing of the burn for S. aureus 999, while for P. aeruginosa, the reduction was more expressive for SS treatment. In the burn tissue, HAgNP + OEO1 treatment was more effective against S. aureus 999, while for P. aeruginosa 1461, both formulations were similarly effective. In the Galleria mellonella test, survival rates after 48 h were 84% for the control group (base) and 50% for both HAgNP + OEO1 and SS treatment groups. Conclusions: This study demonstrates that the hydrogel combining antimicrobials is effective against multidrug-resistant microorganisms, offering a promising alternative for the treatment of infected burns.
Keywords: Galleria mellonella; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Staphylococcus aureus; green nanotechnology; oregano essential oil; porcine skin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic and Additive Effect of Oregano Essential Oil and Biological Silver Nanoparticles against Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains.Front Microbiol. 2016 May 23;7:760. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00760. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27242772 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Strategically Combined With Origanum vulgare Derivatives: Antibacterial Mechanism of Action and Effect on Multidrug-Resistant Strains.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 6;13:842600. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.842600. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35602016 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of methods to detect the in vitro activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNP) against multidrug resistant bacteria.J Nanobiotechnology. 2015 Oct 5;13:64. doi: 10.1186/s12951-015-0120-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2015. PMID: 26438142 Free PMC article.
-
Sulopenem: An Intravenous and Oral Penem for the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections Due to Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Drugs. 2022 Apr;82(5):533-557. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01688-1. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35294769 Review.
-
Antibacterial and antibiofilm potential of silver nanoparticles against antibiotic-sensitive and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.Braz J Microbiol. 2021 Mar;52(1):267-278. doi: 10.1007/s42770-020-00406-x. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Braz J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33231865 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Bioactive Cotton, Wool, and Silk Fabrics Functionalized with Origanum vulgare L. for Healthcare and Medical Applications: An In Vivo Study.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 30;17(7):856. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070856. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dyring-Andersen B., Løvendorf M.B., Coscia F., Santos A., Møller L.B.P., Colaço A.R., Niu L., Bzorek M., Doll S., Andersen J.L., et al. Spatially and Cell-Type Resolved Quantitative Proteomic Atlas of Healthy Human Skin. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:5587. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19383-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- Process No. 444036/2023 (Precision Health - Saúde de Precisão)/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- CNPq 141541/2020-2/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- DT-2; 305972/2022-7/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- DT-2; 302271/2023-6/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- CAPES 88887.803735/2023-00/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

