Nanomedicine-Enhanced Radiotherapy for Glioblastoma: Advances in Targeted Therapy and Adaptive Treatment Strategies
- PMID: 40284502
- PMCID: PMC12030262
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040508
Nanomedicine-Enhanced Radiotherapy for Glioblastoma: Advances in Targeted Therapy and Adaptive Treatment Strategies
Abstract
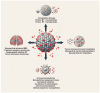
Glioblastoma multiforme remains one of the most aggressive and treatment-resistant brain tumors that necessitate innovative therapeutic approaches. Nanomedicine has emerged as a promising strategy to enhance radiation therapy by improving drug delivery, radiosensitization, and real-time treatment monitoring. Stimuli-responsive nanoparticles can overcome limitations of the blood-brain barrier, modulate tumor microenvironment, and facilitate targeted therapeutic interventions. The integration of nanotechnology with proton and X-ray radiotherapy offers improved dose precision, enhanced radiosensitization, and adaptive treatment strategies. Furthermore, Artificial Intelligence-driven nanoparticle designs are optimizing therapeutic outcomes by tailoring formulations to tumor-specific characteristics. While promising, clinical translation remains a challenge that requires rigorous validation to ensure safety and efficacy. This review highlights advancements in nanomedicine-enhanced radiotherapy and future directions for glioblastoma multiforme treatment.
Keywords: adaptive radiotherapy; blood–brain barrier (BBB); glioblastoma multiforme (GBM); golden nanopeanuts; hypoxia-targeting nanomedicine; immunogenic cell death (ICD); immunotherapy; nanomedicine; personalized oncology; proton therapy; radiosensitization; redox-responsive nanocarriers; stimuli-responsive nanoparticles; tumor microenvironment (TME).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Liu B., Liu J. Surface Modification of Nanozymes. Nano Res. 2017;10:1125–1148. doi: 10.1007/s12274-017-1426-5. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

