Chitosan-Stabilized Lipid Vesicles with Indomethacin for Modified Release with Prolonged Analgesic Effect: Biocompatibility, Pharmacokinetics and Organ Protection Efficacy
- PMID: 40284518
- PMCID: PMC12030005
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040523
Chitosan-Stabilized Lipid Vesicles with Indomethacin for Modified Release with Prolonged Analgesic Effect: Biocompatibility, Pharmacokinetics and Organ Protection Efficacy
Abstract
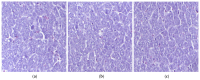
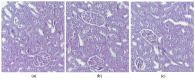
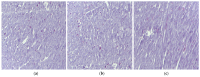
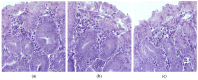
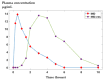
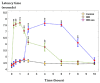
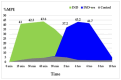
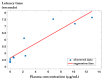
Background/Objectives: Indomethacin (IND) is a widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) effective in managing pain and inflammation. However, its therapeutic use is often limited by gastrointestinal irritation and low bioavailability. This study aimed to evaluate the biocompatibility, release kinetics, and analgesic potential of IND-loaded chitosan (CHIT)-stabilized lipid vesicles (IND-ves) in comparison to free IND, focusing on their in vivo effects and impact on somatic nociceptive reactivity in mice. Methods: IND-ves were prepared using a molecular droplet self-assembly technique, followed by CHIT coating to enhance stability and control drug release. Mice were administered either free IND or IND-ves, and various physiological parameters, including liver and kidney function, oxidative stress markers, immune cell activity, and histopathological changes in key organs, were assessed. Plasma drug release kinetics and analgesic effects were evaluated using the tail-flick test. Results: Both IND and IND-ves demonstrated good biocompatibility, with no significant changes in hematological, biochemical, or immunological profiles. IND-ves exhibited a sustained release profile, with drug release initiating at 30 min and peaking at 3 h, while free IND displayed a rapid release and potential gastric mucosal damage. IND-ves did not induce oxidative stress or inflammation and maintained organ integrity, particularly protecting against gastric injury. Additionally, the prolonged release profile of IND-ves contributed to extended analgesic effects in the tail-flick test. Conclusions: CHIT-stabilized lipid vesicles offer a promising drug delivery system for IND, enhancing drug release, prolonging analgesic efficacy, and minimizing gastrointestinal irritation. These findings suggest that IND-ves could serve as a safer and more effective alternative for NSAID therapy.
Keywords: biocompatibility; indomethacin; lipid vesicles; mice; tail flick.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that they have no financial interests or personal relationships that could have impacted the work presented in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced Stability and In Vitro Biocompatibility of Chitosan-Coated Lipid Vesicles for Indomethacin Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Dec 9;16(12):1574. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121574. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39771553 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, Characterization and Biocompatibility Evaluation of Novel Chitosan Lipid Micro-Systems for Modified Release of Diclofenac Sodium.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 4;11(2):453. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020453. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830989 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of two polymeric matrices for indomethacin in cutaneous nociceptive reactivity in mice.Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2014 Jan-Mar;118(1):125-32. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2014. PMID: 24741788
-
Co-delivery of indomethacin and uricase as a new strategy for inflammatory diseases associated with high uric acid.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Jul;14(7):1820-1838. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01487-5. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38127247
-
Lipid Formulations and Bioconjugation Strategies for Indomethacin Therapeutic Advances.Molecules. 2021 Mar 12;26(6):1576. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061576. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33809343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ewii U.E., Onugwu A.L., Nwokpor V.C., Akpaso I., Ogbulie T.E., Aharanwa B., Chijioke C., Verla N., Iheme C., Ujowundu C., et al. Novel drug delivery systems: Insight into self-powered and nano-enabled drug delivery systems. Nano TransMed. 2024;3:100042. doi: 10.1016/j.ntm.2024.100042. - DOI
-
- Mustafa M.A., Rasheed N., Islam M., Irshad I., Noor-ul-Ain, Batool S., Naveed M., Bibi G., Nazeer J., Wajid F., et al. Advancements in novel drug delivery systems: Techniques for pre and post formulation analysis. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2024;36:142–153. doi: 10.9734/jpri/2024/v36i87565. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

