Mechanisms Underlying the Effects of Secretory Protein G22 on Biological Characteristics and Virulence of Streptococcus suis
- PMID: 40284611
- PMCID: PMC12029192
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13040774
Mechanisms Underlying the Effects of Secretory Protein G22 on Biological Characteristics and Virulence of Streptococcus suis
Abstract
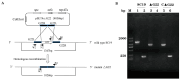
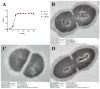
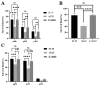
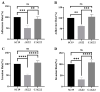
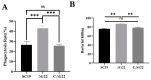
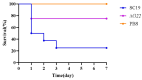
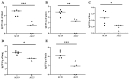
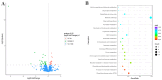
Streptococcus suis serotype 2 (SS2) is an important zoonotic pathogen that seriously harms the swine industry and human health. However, its pathogenic mechanisms are largely unknown, and the few virulence factors reported so far are insufficient to systematically explain its infectious and pathogenic mechanisms. In preliminary research, we identified a gene named G22 encoding a hypothetical secreted protein that may be closely associated with the high-level pathogenicity of S. suis. In this study, we constructed deletion and complementation strains of the G22 gene through homologous recombination and explored its roles in the pathogenicity and susceptibility of S. suis to environmental stresses through in vitro and in vivo experiments. The deletion of G22 clearly influenced the typical capsular structure of SS2 and impaired the bacterium's growth in a medium containing hydrogen peroxide (showing a growth reduction of 32.98% ± 5.23% compared to the wild-type strain SC19, p < 0.001) or with a low pH (with a growth inhibition of 17.44% ± 1.9% relative to the wild-type strain SC19, p < 0.01). ΔG22 also showed reduced survival in whole blood and in RAW 264.7 macrophages (with a survival reduction of 16.44% ± 2.29% compared to the wild-type, p < 0.001). The deletion of G22 also sharply attenuated the virulence of SS2 in a mouse infection model (reducing the mortality rate by 50% ± 0.04%, p < 0.05). We also demonstrated that G22 is required for the adhesion and invasion of SS2 in host cells. An RNA sequencing analysis revealed that 50 genes were differentially expressed in the ΔG22 and wild-type strains: 23 upregulated and 37 downregulated. Many of the genes are involved in carbohydrate metabolism and the synthesis of virulence-associated factors. Several genes associated with the phosphotransferase system were significantly upregulated in strain ΔG22. In summary, G22 plays a role in the morphological development and pathogenesis of the highly virulent SS2 strain SC19.
Keywords: G22; Streptococcus suis; bacterial virulence; gene knockout; transcriptome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors state that they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SBP1 is an adhesion-associated factor without the involvement of virulence in Streptococcus suis serotype 2.Microb Pathog. 2018 Sep;122:90-97. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.06.008. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29886087
-
Exogenous glycogen utilization effects the transcriptome and pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis serotype 2.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 9;12:938286. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.938286. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36439226 Free PMC article.
-
The Redox-Sensing Regulator Rex Contributes to the Virulence and Oxidative Stress Response of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Sep 18;8:317. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00317. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30280091 Free PMC article.
-
The biological role of MutT in the pathogenesis of the zoonotic pathogen Streptococcus suis serotype 2.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):1538-1549. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1936770. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34077309 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus suis: a re-emerging pathogen associated with occupational exposure to pigs or pork products. Part II - Pathogenesis.Ann Agric Environ Med. 2018 Mar 14;25(1):186-203. doi: 10.26444/aaem/85651. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2018. PMID: 29575852 Review.
References
-
- Gottschalk M., Segura M., Xu J. Streptococcus suis infections in humans: The Chinese experience and the situation in North America. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2007;8:29–45. - PubMed
-
- Nahuel F., Mariela S., Daniel G., Marcelo G. Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis. Future Microbiol. 2012;7:259–279. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

