Regulation of Ergosterol Biosynthesis in Pathogenic Fungi: Opportunities for Therapeutic Development
- PMID: 40284698
- PMCID: PMC12029249
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13040862
Regulation of Ergosterol Biosynthesis in Pathogenic Fungi: Opportunities for Therapeutic Development
Abstract
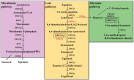
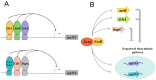
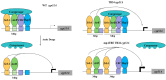
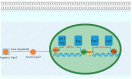
Ergosterol plays a dual role in fungal pathogenesis and azole resistance, driving key advancements in the understanding of its biosynthesis regulation. This review integrates the latest research progress on the regulation of fungal ergosterol biosynthesis and its role in drug resistance and pathogenicity. We comprehensively discuss the functions of key enzymes (such as Erg11p/Cyp51A, Erg6p, Erg3p, and Erg25p) in the mevalonate, late, and alternative pathways. Notably, we highlight the complex regulation of cyp51A expression by factors such as SrbA, AtrR, CBC, HapX, and NCT in Aspergillus fumigatus, and elucidate the distinctive roles of Upc2, Adr1, and Rpn4 in Candida species. Importantly, we summarize recent discoveries on the CprA-dependent regulation of Cyp51A/Erg11p and heme-mediated stability control. Based on these findings, we propose innovative antifungal strategies, including dual-target inhibition and multi-enzyme inhibition by natural products, which provide novel insights and potential directions for the development of next-generation antifungal therapies.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; antimicrobial resistance; erg11A/cyp51A; ergosterol biosynthesis; pathogenic fungi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Novel Zn2-Cys6 Transcription Factor AtrR Plays a Key Role in an Azole Resistance Mechanism of Aspergillus fumigatus by Co-regulating cyp51A and cdr1B Expressions.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jan 4;13(1):e1006096. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006096. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28052140 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-specific transcriptional activation by the Aspergillus fumigatus AtrR factor requires a conserved C-terminal domain.mSphere. 2024 Jul 30;9(7):e0042524. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00425-24. Epub 2024 Jul 8. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38975761 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of High-Affinity Iron Acquisition, Including Acquisition Mediated by the Iron Permease FtrA, Is Coordinated by AtrR, SrbA, and SreA in Aspergillus fumigatus.mBio. 2023 Jun 27;14(3):e0075723. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00757-23. Epub 2023 Apr 24. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37093084 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance in human pathogenic yeasts and filamentous fungi: prevalence, underlying molecular mechanisms and link to the use of antifungals in humans and the environment.Dan Med J. 2016 Oct;63(10):B5288. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27697142 Review.
-
Regulation of Sterol Biosynthesis in the Human Fungal Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus: Opportunities for Therapeutic Development.Front Microbiol. 2017 Feb 1;8:92. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00092. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28203225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the therapeutic mechanism of itraconazole combined with ritonavir on Candida albicans infection through network pharmacology and molecular docking.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 14;16:1578749. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1578749. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40727105 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing thiazole chemistry for antifungal strategies through an experimental and computational chemistry approach: anti-biofilm, molecular docking, dynamics, and DFT analysis.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 26;15(27):21838-21858. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00657k. eCollection 2025 Jun 23. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40575561 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 31800058/he National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024XKT1519/the Innovation Project for College Graduates of Jiangsu Province
- LMS25C010003/the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- GXHCFM2023014, 23-026-15/the Guangxi Key Laboratory of Mycosis Prevention and Treatment
- AHIDL-2413R/the Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Infectious Diseases at the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

