2002-2022 Quinolone Resistance in Escherichia coli of Swine in Mainland China: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40284847
- PMCID: PMC12031296
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci12040345
2002-2022 Quinolone Resistance in Escherichia coli of Swine in Mainland China: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
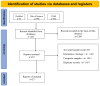
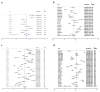
Swine have emerged as significant reservoirs of antibiotic-resistant strains and genes. To establish a sound rationale for applying quinolone antibiotics in the swine industry, a meta-analysis was performed on the resistance rate of swine-derived Escherichia coli to quinolone antibiotics in China from 2002 to 2022. We systematically searched through three databases, PubMed, Web of Science, and CNKI, and included 53 eligible studies within the specified timeframe. Resistance rates were calculated using a random-effects model and the Freeman-Tukey double-arcsine transformation. The resistance rates observed were as follows: 37% for levofloxacin (95% CI: 27~47%), 43% for ofloxacin (95% CI: 34~51%), 54% for enrofloxacin (95% CI: 46~62%), and 50% for ciprofloxacin (95% CI: 42~58%). Further subgroup analyses illuminated that the resistance rates were higher in mainland China's eastern regions than in western regions. Additionally, there was no significant decrease in the resistance rate over time in different periods. From 2002 to 2022, Escherichia coli strains from swine in various regions of mainland China exhibited differing degrees of generalized resistance to quinolones. This poses a potential public health risk and underscores the fact that the control of quinolone antibiotics remains a prolonged and ongoing challenge.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; antibiotic resistance; meta-analysis; quinolone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mitra S.D., Shome R., Bandopadhyay S., Geddam S., Kumar A.M.P., Murugesan D., Shome A., Shome B.R. Genetic insights of antibiotic resistance, pathogenicity (virulence) and phylogenetic relationship of Escherichia coli strains isolated from livestock, poultry and their handlers—A one health snapshot. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024;51:404. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09354-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- García-Meniño I., García V., Alonso M.P., Blanco J.E., Blanco J., Mora A. Clones of enterotoxigenic and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli implicated in swine enteric colibacillosis in Spain and rates of antibiotic resistance. Vet. Microbiol. 2021;252:108924. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108924. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

