Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Variant Infection Dynamics and Pathogenesis in Transgenic K18-h ACE2 and Inbred Immunocompetent C57BL/6J Mice
- PMID: 40284943
- PMCID: PMC12031173
- DOI: 10.3390/v17040500
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Variant Infection Dynamics and Pathogenesis in Transgenic K18-h ACE2 and Inbred Immunocompetent C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
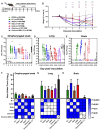
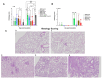
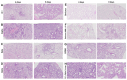
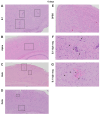
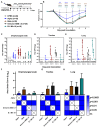
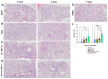
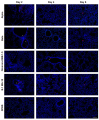
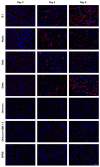
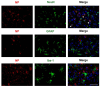
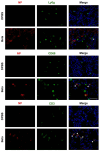
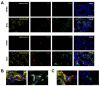
The global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), persists in part due to the emergence of new variants. Understanding variant-specific infection dynamics and pathogenesis in murine models is crucial for identifying phenotypic changes and guiding the development of countermeasures. To address the limitations of earlier studies that investigated only a few variants or used small sample sizes, we evaluated clinical disease, infection kinetics, viral titers, cellular localization, and histopathologic changes in the lungs and brains of transgenic B6.Cg-Tg(K18-ACE2)2Prlmn/J ("K18") and corresponding genetic control (C57BL/6J) mice expressing human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2). Six SARS-CoV-2 variants were assessed: B.1 (WA1-like), alpha, beta, delta, omicron, and omicron XBB.1.5, using cohorts of ≥18 mice. Following intranasal inoculation with B.1, alpha, beta, or delta variants, K18 mice experienced rapid weight loss and reached euthanasia criteria by 5-6 days post-inoculation (dpi). In contrast, K18 mice inoculated with both omicron variants recovered to their starting weight within 4-6 dpi. Infectious SARS-CoV-2 was detected in the oropharynx at 1 and2 dpi, in the lungs at 2, 4, and 6 dpi, and in the brain at 4 and 6 dpi for all variants except omicron. SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein was detected, and interstitial pneumonia of varying severity was observed in K18 mice infected with all variants. Brain lesions were identified in mice infected with the B.1, beta, and delta variants 6 dpi. As K18 mice express hACE2 in the brain-a feature not present in humans-we also compared infection dynamics of three variants to those of a mouse-adapted WA1 strain in C57BL/6J mice lacking the human ACE2 gene. C57BL/6J mice did not experience lethal disease, exhibited milder pneumonia, and had no evidence of neuroinvasion despite similar infection kinetics to K18 mice. These findings demonstrate contrasting phenotypes across the two models and reduced tropism and pathology of omicron compared to earlier variants in both models. This comprehensive analysis of SARS-CoV-2 variants in two mouse models provides valuable insights for model and variant selection for future studies.
Keywords: C57BL/6J mice; COVID-19; K18 mice; SARS-CoV-2; human ACE2 receptor-expressing mice; infection dynamics; mouse model; pathogenesis; transgenic mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Establishment and characterization of an hACE2/hTMPRSS2 knock-in mouse model to study SARS-CoV-2.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 10;15:1428711. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1428711. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39050847 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal Characterization of Changes in the Respiratory Tract and the Nervous System, Including the Eyes in SARS-CoV-2-Infected K18-hACE2 Mice.Viruses. 2025 Jul 9;17(7):963. doi: 10.3390/v17070963. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40733579 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclast-mediated bone loss observed in a COVID-19 mouse model.Bone. 2022 Jan;154:116227. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2021.116227. Epub 2021 Oct 2. Bone. 2022. PMID: 34607050 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-neutralising monoclonal antibodies to prevent COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 17;6(6):CD014945. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014945.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35713300 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- COVID-19 Cases|WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. [(accessed on 22 October 2024)]. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases.
-
- World Health Organization . Post COVID-19 Condition (Long COVID) World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2025.
-
- Tarrés-Freixas F., Trinité B., Pons-Grífols A., Romero-Durana M., Riveira-Muñoz E., Ávila-Nieto C., Pérez M., Garcia-Vidal E., Perez-Zsolt D., Muñoz-Basagoiti J., et al. Heterogeneous Infectivity and Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Beta, Delta and Omicron in Transgenic K18-hACE2 and Wildtype Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022;13:840757. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.840757. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

