E5 Oncoprotein: A Key Player in Human Papillomavirus-Positive Head and Neck Cancer Pathogenesis and Therapy Resistance
- PMID: 40284955
- PMCID: PMC12031384
- DOI: 10.3390/v17040512
E5 Oncoprotein: A Key Player in Human Papillomavirus-Positive Head and Neck Cancer Pathogenesis and Therapy Resistance
Abstract
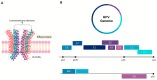
Head and neck cancer (HNC) is the sixth most prevalent type of cancer worldwide and is associated with low five-year survival rates. Alcoholism and smoking are the main risk factors associated with the development of head and neck cancer (HNC). However, Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection has been reported as a significant risk factor, particularly for the oropharyngeal subset. In these cases, patients with HPV-positive HNC exhibit a better clinical prognosis; however, resistance to chemotherapy has been frequently reported. The carcinogenic activity of HPV is related to the viral oncoproteins E5, E6, and E7. E5 has been associated with immune evasion mechanisms and modulation of the tumor microenvironment, which appears to be linked to the virus's resistance to chemotherapeutic treatments. Here, we review the potential of HPV E5 in targeted therapy for HNC and discuss relevant data regarding the activity of this oncoprotein in head and neck carcinogenesis.
Keywords: HNC; human papillomavirus; immune evasion; oncoprotein; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Current status of circulating tumor DNA and circulating cell alterations in HPV-associated head and neck cancer.Oral Oncol. 2025 Aug;167:107417. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2025.107417. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Oral Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40516153 Review.
-
Viral Transcript and Tumor Immune Microenvironment-Based Transcriptomic Profiling of HPV-Associated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Identifies Subtypes Associated with Prognosis.Viruses. 2024 Dec 24;17(1):4. doi: 10.3390/v17010004. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39861794 Free PMC article.
-
The Differential Expression of the JAK/STAT Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells Transfected with Human Papillomavirus Oncogenes.Viruses. 2025 Jun 23;17(7):880. doi: 10.3390/v17070880. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40733498 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and transcriptomic profiling in exosomes derived from HPV-positive head and neck cancer.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Aug 30;776:152188. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.152188. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40517673
-
A systematic literature review of the human papillomavirus prevalence in locally and regionally advanced and recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancers through the last decade: The "ALARM" study.Cancer Med. 2024 Feb;13(3):e6916. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6916. Epub 2024 Jan 21. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38247106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kühn J.P., Schmid W., Körner S., Bochen F., Wemmert S., Rimbach H., Smola S., Radosa J.C., Wagner M., Morris L.G.T., et al. HPV Status as Prognostic Biomarker in Head and Neck Cancer—Which Method Fits the Best for Outcome Prediction? Cancers. 2021;13:4730. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184730. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Makarewicz J., Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka K., Sobocki B.K., Dobrucki I.T., Kalinowski L., Stachowska E. Anti-Cancer Management of Head and Neck Cancers and Oral Microbiome-What Can We Clinically Obtain? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024;14:1329057. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1329057. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muniz I.D.A.F., Araujo M., Bouassaly J., Farshadi F., Atique M., Esfahani K., Bonan P.R.F., Hier M., Mascarella M., Mlynarek A., et al. Therapeutic Advances and Challenges for the Management of HPV-Associated Oropharyngeal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024;25:4009. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 444606/2023-8/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- 444156/2023-2/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- 308684/2023-0/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- APQ-0806-2.02/24/Fundação de Amparo à Ciência e Tecnologia de Pernambuco
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

