Metacarpophalangeal pattern profile analysis in Prader-Willi syndrome. A follow-up report on 38 cases
- PMID: 4028497
- PMCID: PMC6706852
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb01213.x
Metacarpophalangeal pattern profile analysis in Prader-Willi syndrome. A follow-up report on 38 cases
Abstract
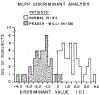
Metacarpophalangeal pattern profile (MCPP) was determined on 38 Prader-Willi syndrome individuals and compared with a previous report on 16 patients. Chromosome analysis showed an interstitial deletion of the long arm of chromosome 15 in 20 subjects and normal chromosome results in the remaining 18 individuals. The mean hand profile of 38 individuals was essentially flat while the profiles for the two groups based on chromosome findings were separate in the metacarpal area. Correlation studies confirmed the homogeneity of the deletion group relative to Prader-Willi syndrome individuals with normal chromosomes. Discriminant analysis of Prader-Willi syndrome versus control individuals produced a function of three MCPP variables plus age which may be applied as another diagnostic tool.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical